91 Maps
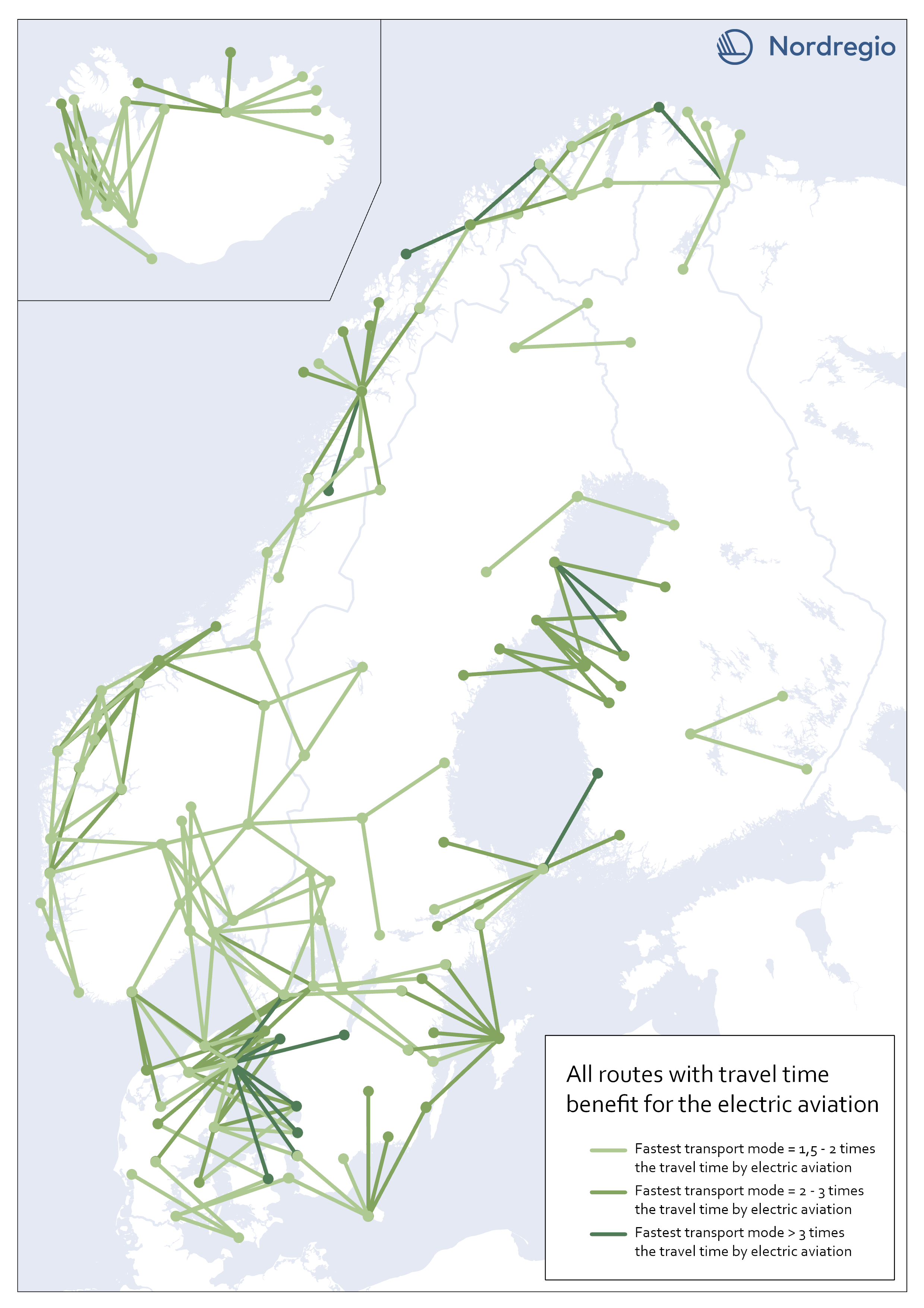
All routes with time benefit for electric aviation
The map shows all routes in our sample with significant travel time benefit for electric aviation. They are 203 in total. A route has a significant travel time benefit if the travel time for both car and public transportation exceeded 1,5 times the travel time for electric aviation. I.e., if one of the existing transport modes is faster or up to 1,5 times the travel time for electric aviation, electric aviation does not have the potential to improve accessibility between the two destinations, according to our analysis.
2023 February
- Nordic Region
- Transport
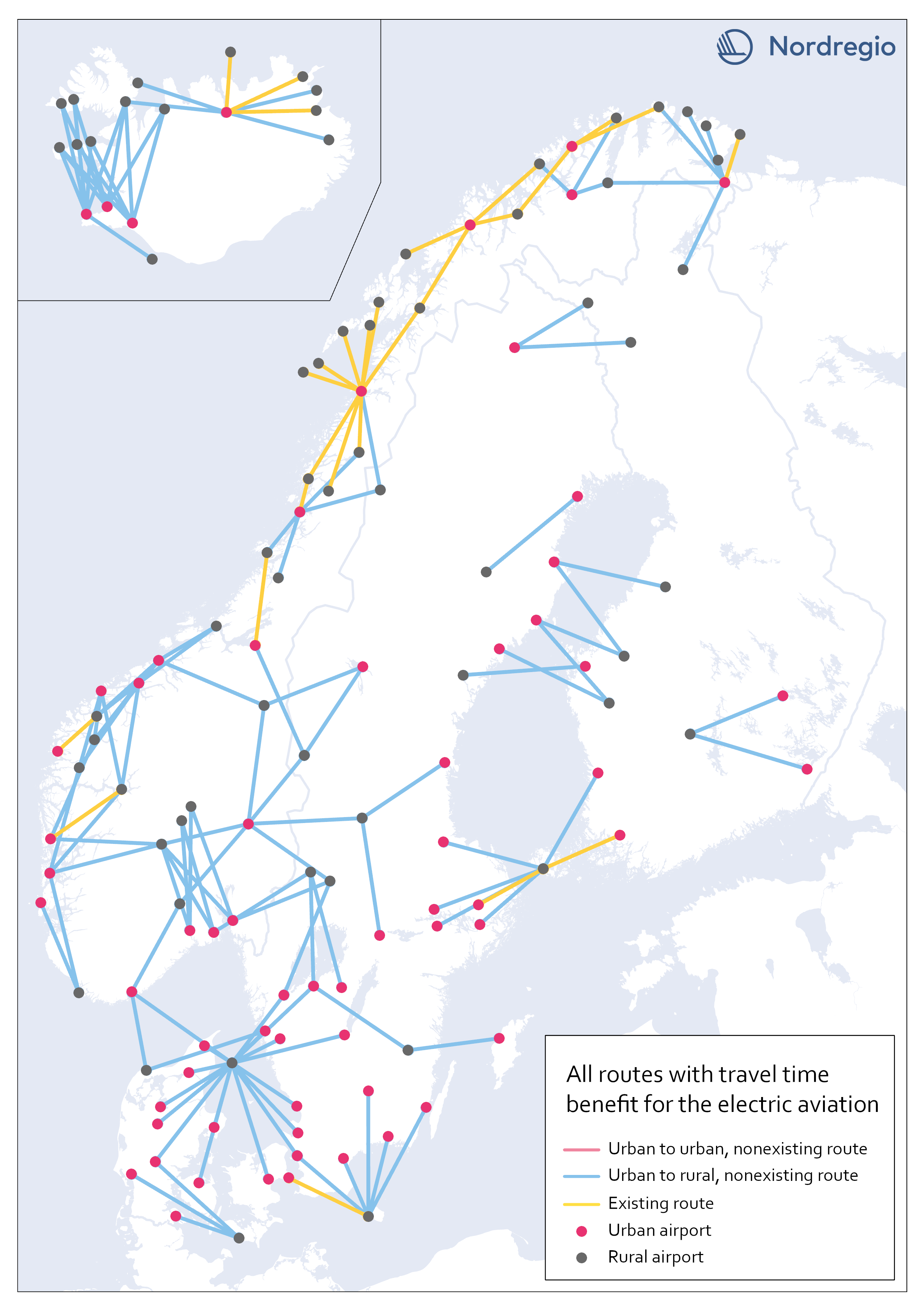
Electric aviation time benefits between urban and rural areas
The map shows all routes between urban and rural areas where electric aviation has significant time benefits compared to other traffic modes. Yellow lines are already served by aviation, while blue color indicates non-existent routes where electric flight would reduce the travel time between destinations. Our motivation for focusing on urban-rural routes was based on the assumption that electric aviation can increase the access for rural areas to public facilities and job opportunities, as well as the possibility of connecting remote areas with national and international transport systems. The result, though, can only be understood in terms of travel time benefits between the areas, and thus reveals little about accessibility to mentioned opportunities. The following are examples of themes to be investigated further within the main project. Identify regional hubs Among others, the project FAIR (2022) has addressed the need to update the flight system to a more flexible aviation network, that meet travelers’ needs with smart mobility. This can be done by identifying demands and establishing regional hubs for electric aviation, which can serve remote and regional areas. The potential of Hamar and Bodö in Norway as regional hubs should be studied more closely.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
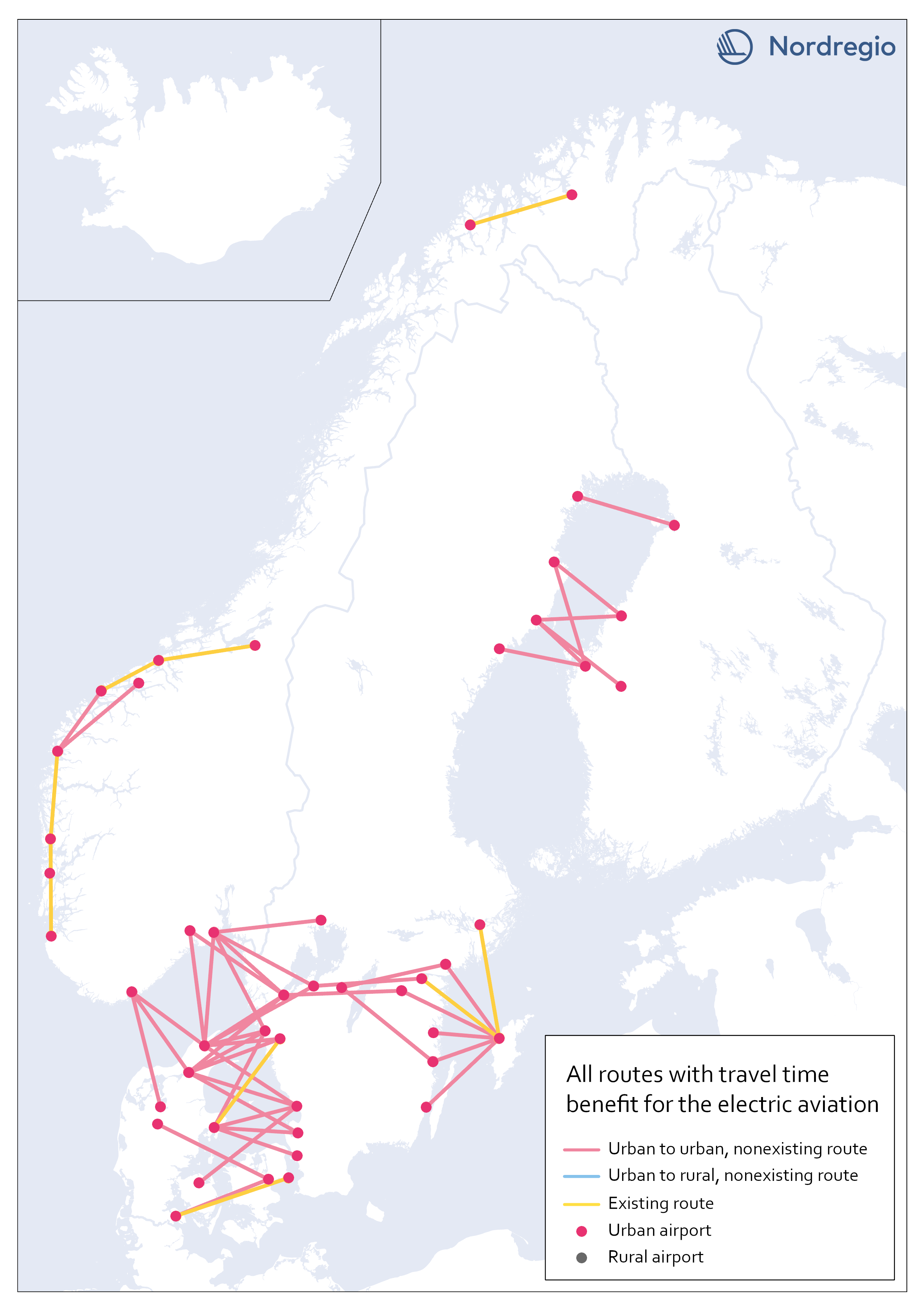
Electric aviation time benefits between urban areas separated by water
The map shows all routes between urban areas separated by water, and where electric aviation has significant time benefits compared to the fastest traffic mode. Yellow lines are already served by aviation, while red color indicates non-existent routes where electric flight would reduce the travel time between destinations. The result is in line with our assumptions, that there is a lack of fast connections between potential labor markets in urban areas, which are geographically close but separated by open water.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
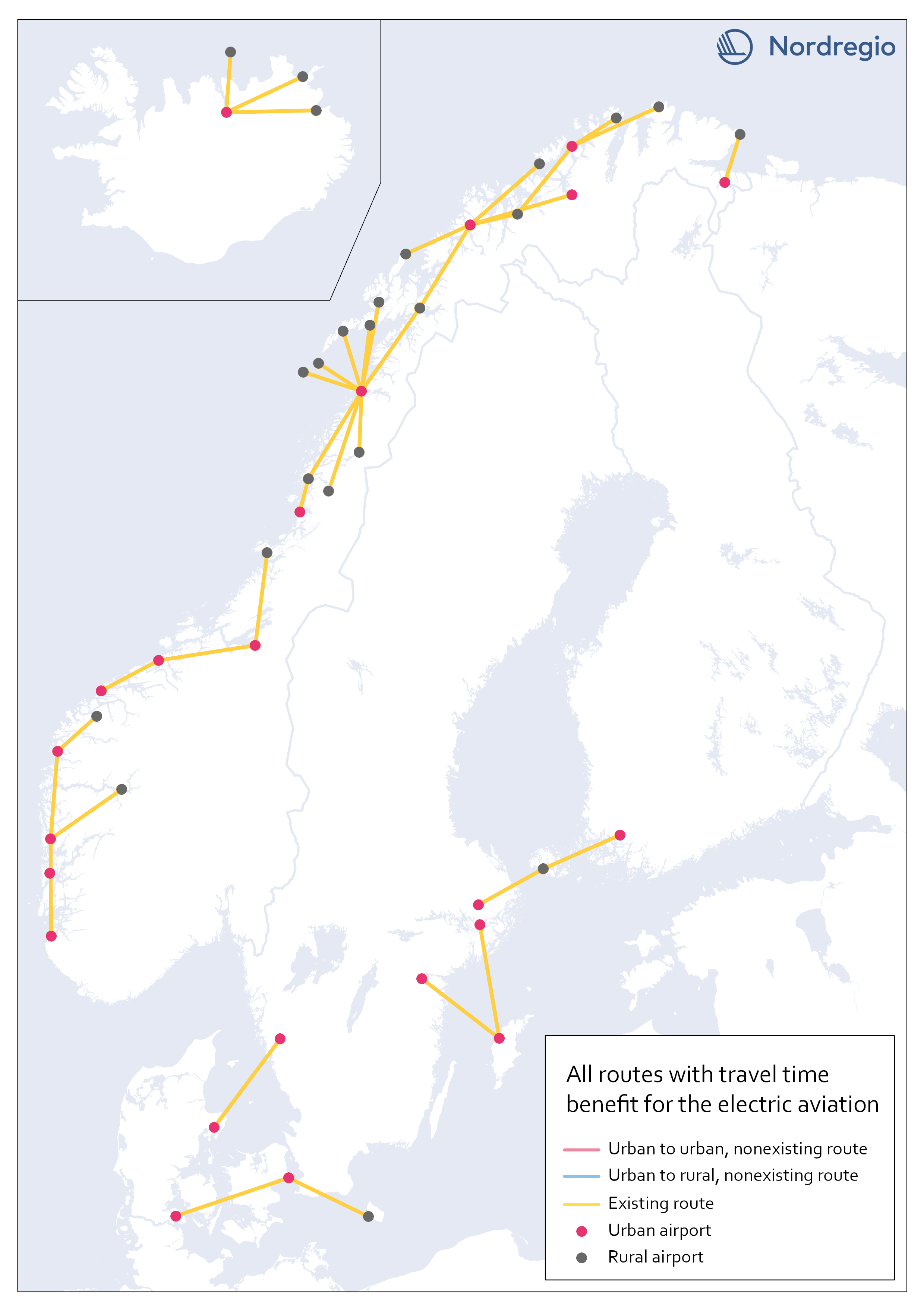
Existing routes with time benefit for electric aviation
The map visualizes all routes with significant travel time benefit, which are already served with commercial flights. Information on existing routes has been obtained from the report Nordic Sustainable Aviation (Ydersbond et al, 2020) and applies to the year 2019. Since then, routes may have been added or removed, which is important to bear in mind in future investigations. However, choosing a later year risk giving equally misleading results, as flights decreased drastically during the pandemic. Statistics for 2019 provide a picture of the demand that existed before the pandemic, which is the latest stable levels that can be obtained. Whether air traffic will ever return to the same levels as before the pandemic is too early to say. The majority of routes are found in Norway, along the coastline, which confirms earlier knowledge that Norway has a more extensive and coherent aviation network than the rest of the Nordic region.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
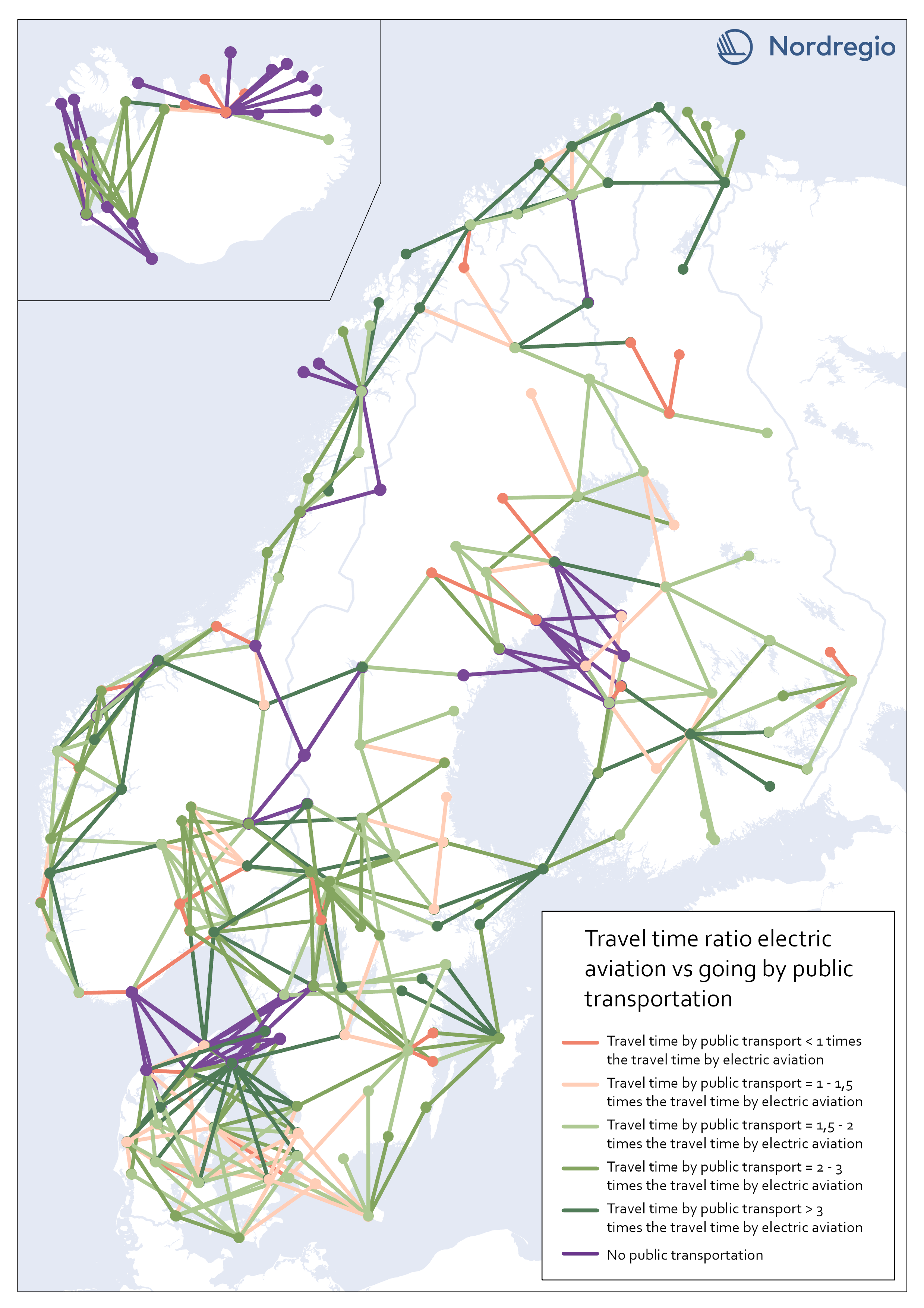
Travel time ratio – electric aviation vs public transportation
This map shows the travel time calculations for electric aviation versus travelling by public transportation. Routes represented by any nuance of green, are routes with significant travel time benefits for electric aviation in comparison with public transportation. The darker the nuance of green, the larger time benefit for electric aviation. The beige color represents routes where the travel time for public transportation is the same or up to 1,5 times the travel time for electric aviation. The red color represents routes where public transportation is faster than electric aviation. Purple lines represent routes where no public transportation is available. These were also routes where we could see significant time benefits for electric aviation. The number of changes when commuting with public transport may have a negative impact on perceived accessibility. In this accessibility analysis, however, we stay with the same criteria for public transport as for travel by car. For future research, the number of changes when commuting by public transport could be considered in the comparison.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
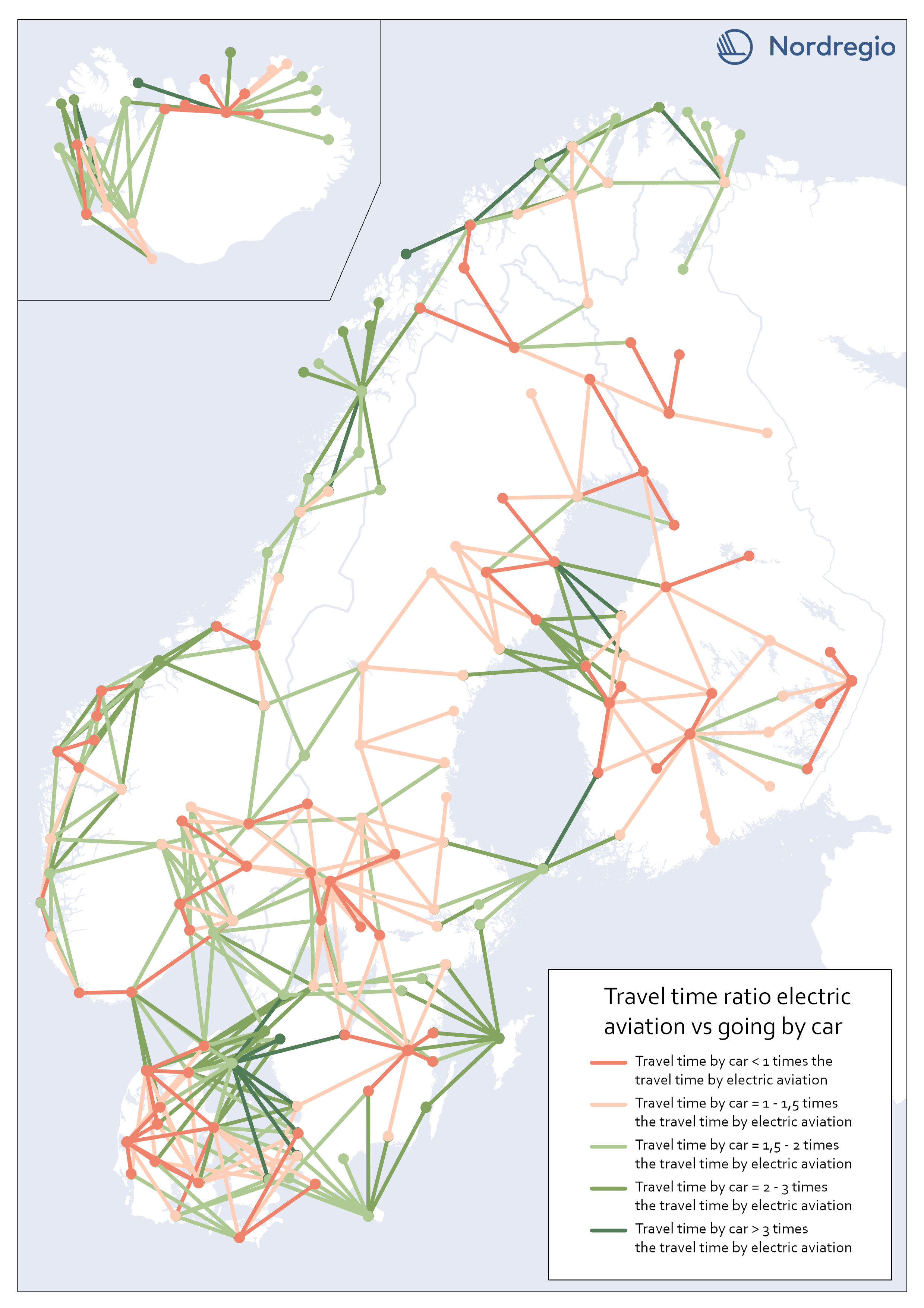
Travel time ratio – electric aviation vs car
This map shows the travel time calculations for electric aviation versus traveling by car. Routes represented by any nuance of green, are routes with significant travel time benefits for electric aviation in comparison with car. The darker the nuance of green, the larger time benefit for electric aviation. The beige color represents routes where the travel time for car is the same or up to 1,5 times the travel time for electric aviation. The red color represents routes where car is faster than electric aviation.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
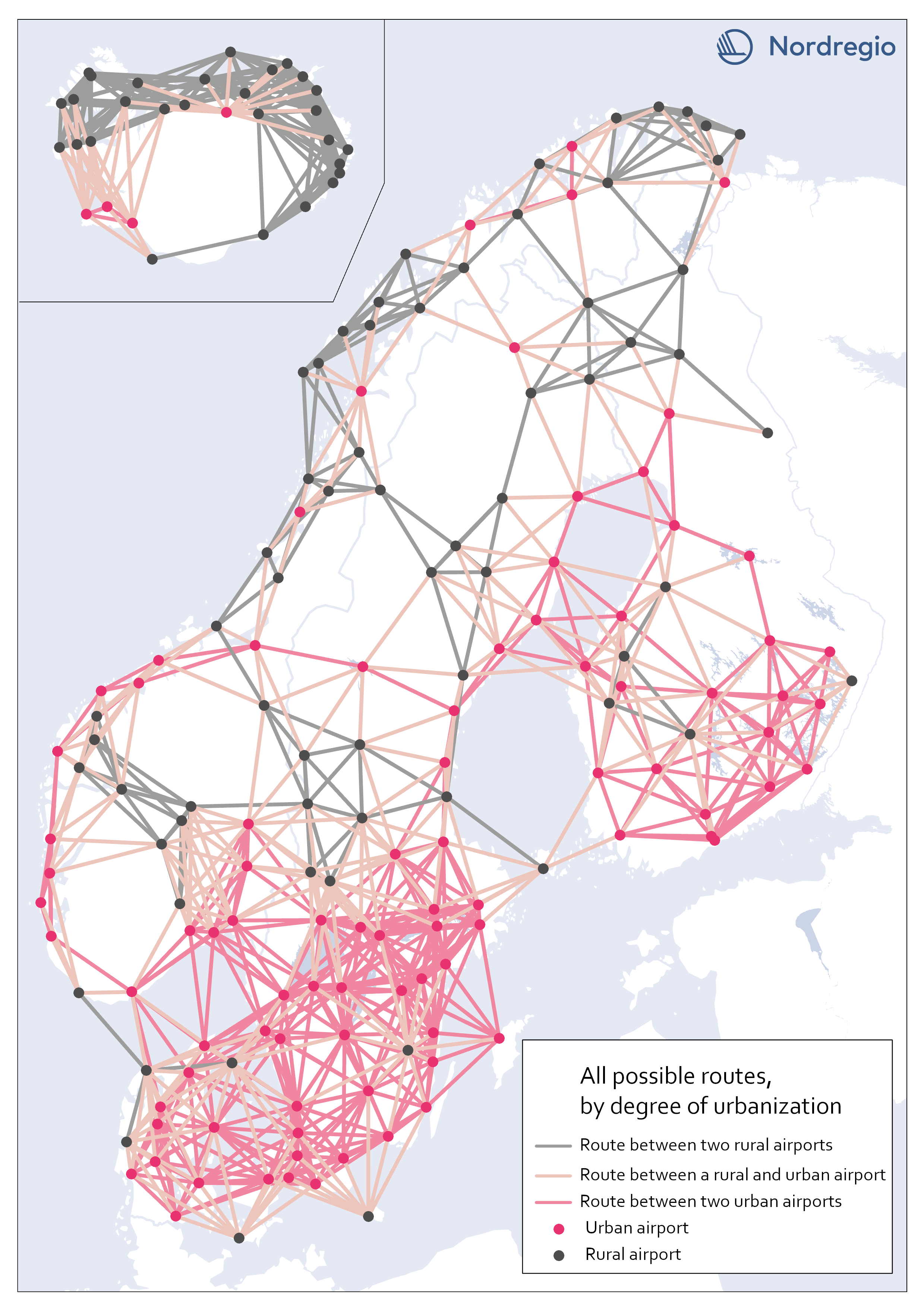
All possible electric aviation routes by a degree of urbanisation
The map shows all routes with a maximum distance of 200 km divided into three categories, based on the airports’ degree of urbanization: Routes between two rural airports, routes between one rural and one urban airport and routes between two urban airports. The classification is based on the new urban-rural typology. We restricted the analysis to routes between rural and urban areas as well as routes between urban areas that are separated by water. Those are 426 in total. We based our criteria on the assumption that accessibility gains to public services and job clusters can be made for rural areas, if better connected to areas with a high degree of urbanization. Because of possible potential to link labor markets between urban areas on opposite sides of water urban to urban areas that cross water are also included. This is based on previous research which has shown the potential for electric aviation to connect important labor markets which are separated by water, particularly in the Kvarken area (Fair, 2022). Our choice of selection criteria means that we intentionally ignore routes where electric aviation may have a potential to reduce travel times significantly. There might also be other important reasons for the implementation of electric aviation between the excluded routes. Between rural areas, for example, tourism or establishing a comprehensive transport system in the Nordic region, constitute reasons for implementing electric aviation. Regarding routes between urban areas over mainland, the inclusion of more routes with the same rationale as above – that significant time travel benefits could be gained between labor markets with electric aviation (for example between two urban areas in mountainous regions where travel times can be long) – can be motivated. Some of those routes can be important to investigate at a later stage but are outside the…
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
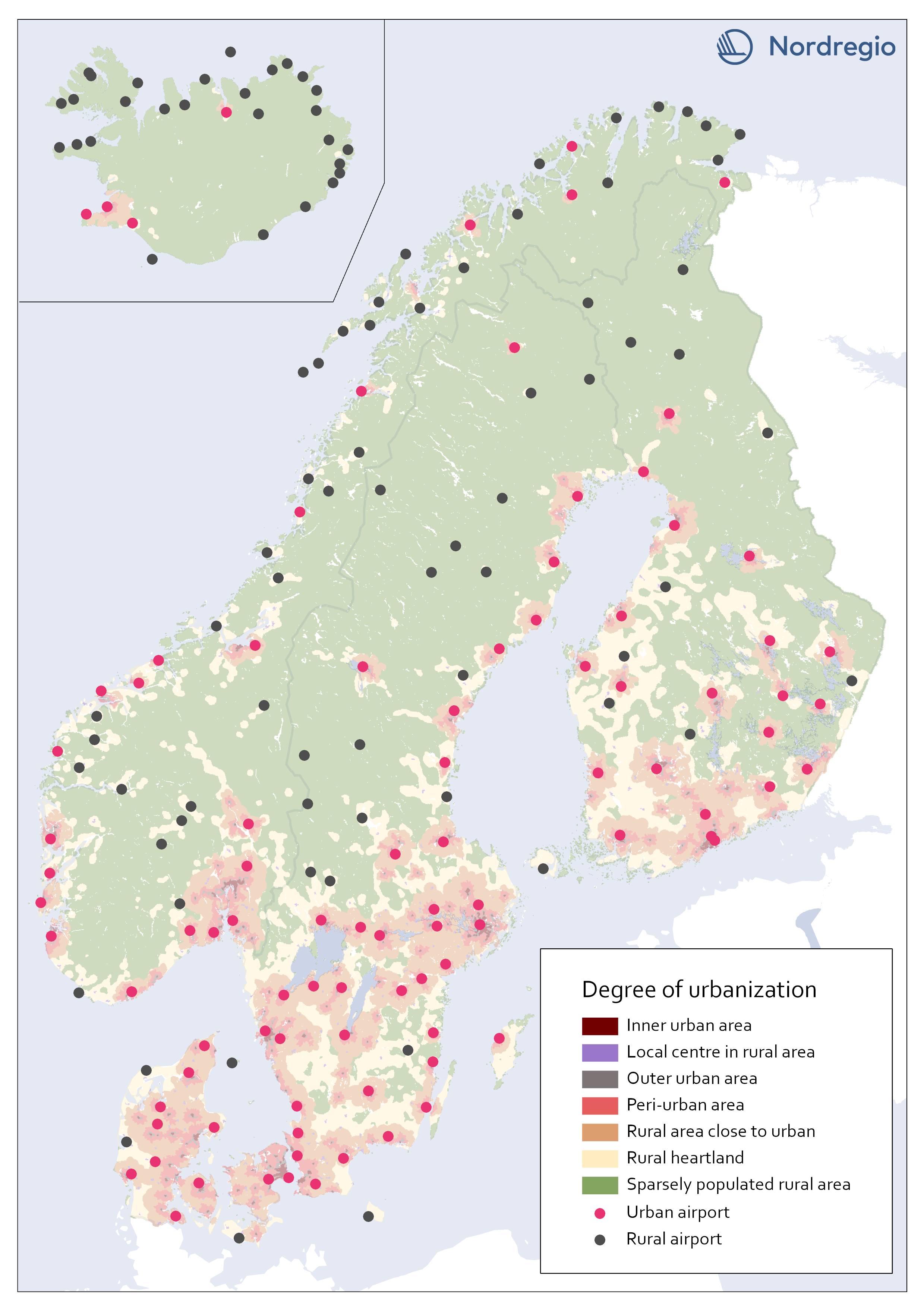
All airports in the Nordic region by a degree of urbanisation
This map classifies all airports by a degree of urbanisation. The classification is based on the new urban-rural typology. We classified all airports localized within any of the top five urbanization classes (Inner urban area, Local center in rural area, Outer urban area, peri-urban area, or Rural area close to close to urban) as Urban. All other airports, localized within the bottom two classes (Rural heartland or Sparsely populated rural area) were classified as Rural. No adjustments were made based on the proximity of the airports to urban areas. During the process we considered adjustments in the categorization based on the airports’ potential catchment area from a close urban area. For example, one can assume that Gällivare Lappland airport in the north of Sweden, has its main catchment area from Gällivare which is classified as a local center in rural area (i.e. Urban). The airport, though, is localized within the category Rural heartland. Yet, we decided to let the typology determine to which category each airport belong.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
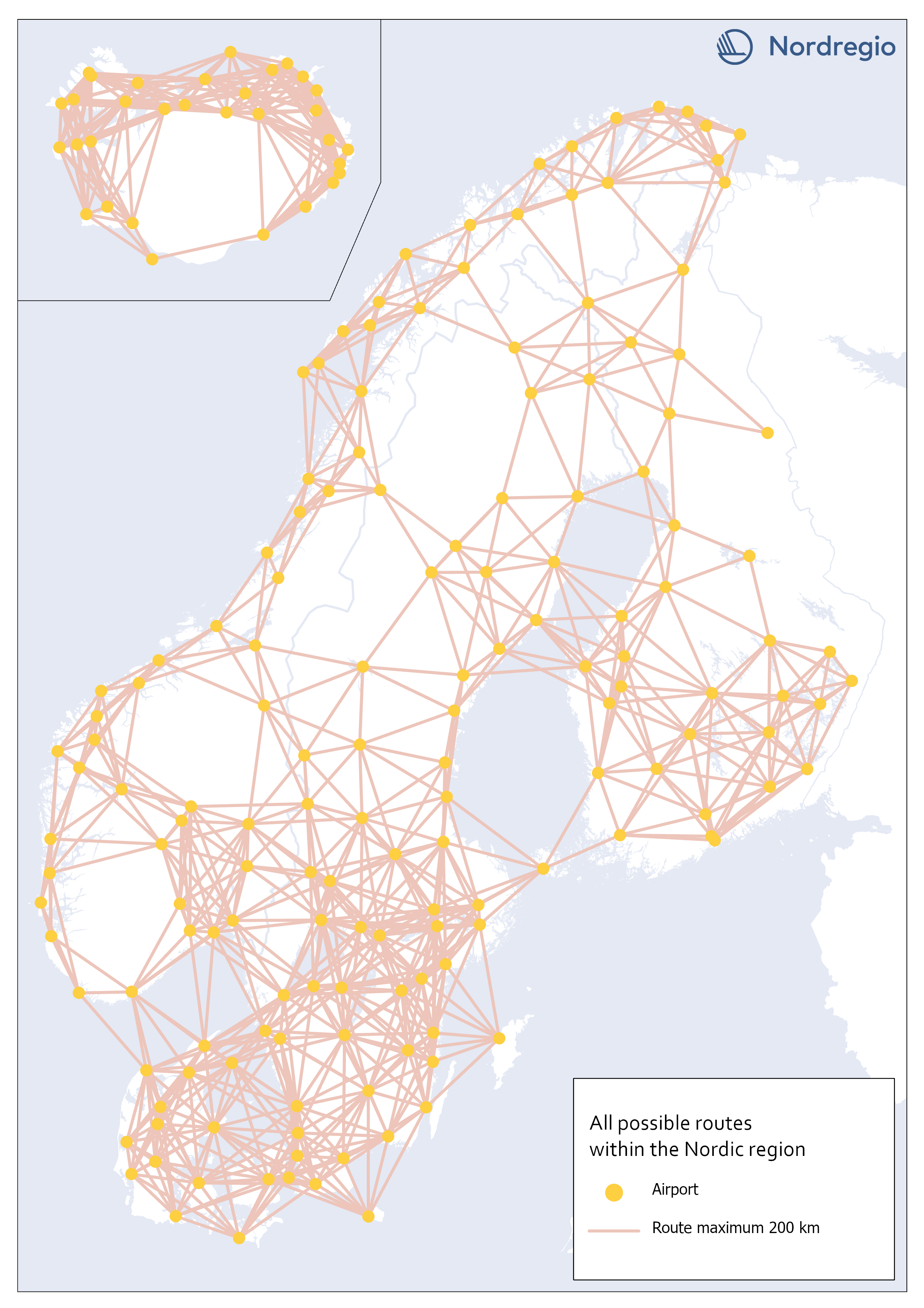
All possible electric aviation routes, max 200km, within the Nordic region
This map shows all possible electric aviation routes of a maximum distance of 200 kilometres within the Nordic region. First generation electric aviation will have a limited range due to battery capacity. According to the report Nordic Sustainable Aviation, routes up to 400 kilometers constitute an initial market for electric airplanes in the Nordic region. However, also shorter distance routes under 200 km, where cruise speed is less important and in sparsely populated regions where passenger volumes are very small, will be the focus (Ydersbond et al, 2020). The first generation of aircrafts that rely solely on electric power have a defined maximum range of 200 km (Heart Areospace, 2022). For this accessibility study, we only included routes of a maximum distance of 200 kilometers. This selection gave us 1001 possible routes in total.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
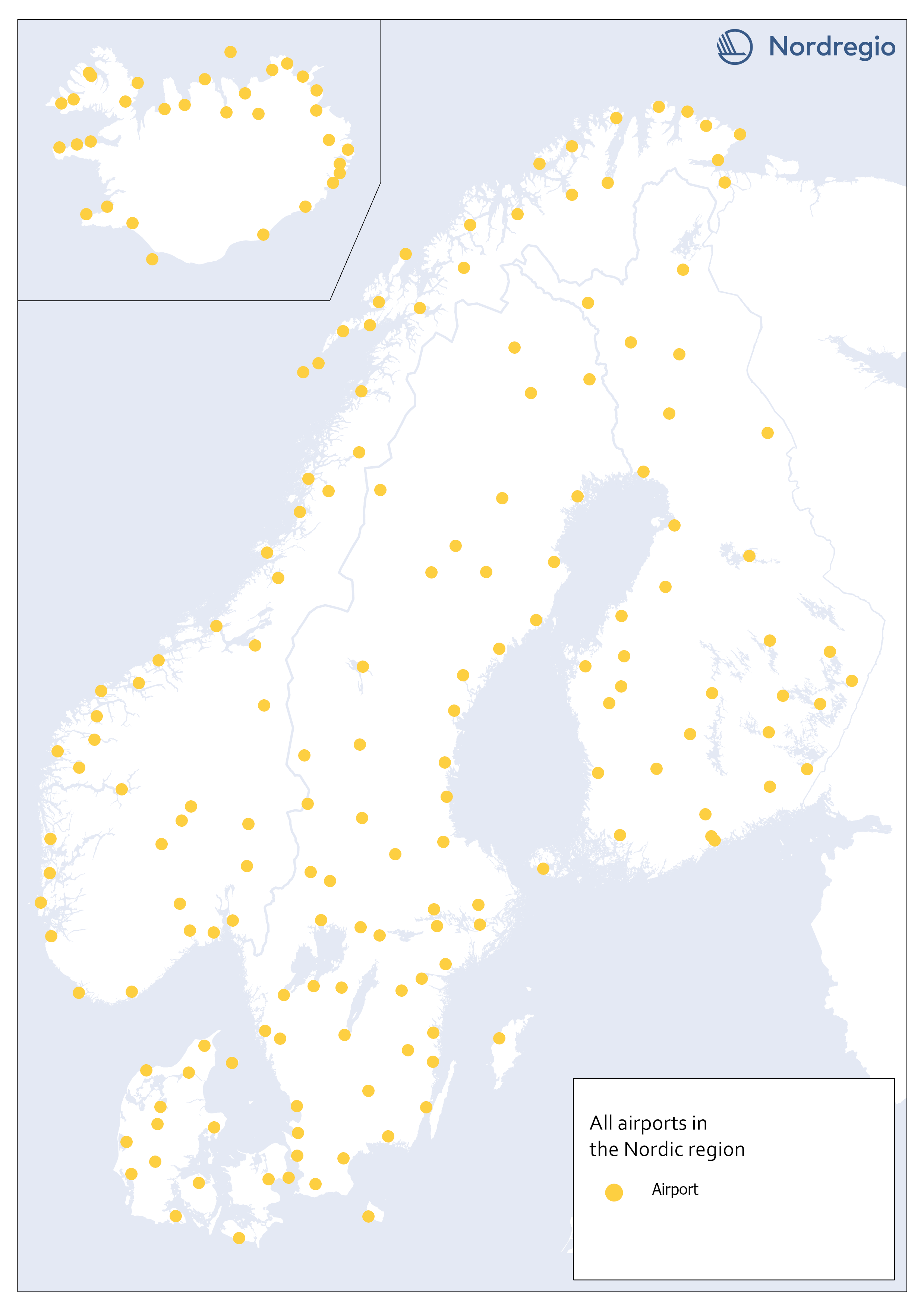
All airports in the Nordic region
This map shows all airports within the geographical scope which may be operated with commercial flight. To limit our selection of airports, we used a combination of two official airport code systems: IATA (International Air Transport Association) and ICAO (International Civil Aviation Organization). IATA-codes specify the airport as a part of a commercial flight route. However, the IATA system, is not solely limited to airports. Other locations, such as bus or ferry stations can also apply for an IATA location code, as long it is included in an airline travel chain. The ICAO-code, on the other hand, indicates that the location is an airport, but not necessarily for commercial flights In order to obtain a selection of airports that met our criteria, an airport was included only if it had both an IATA-code and an ICAO-code. Three different sources are used: 1) Swedavia (lists all airports in the Nordics that Swedavia traffics today). This is our main source, but it does not include all existing airports in the Nordic countries. Therefore, we also use two other sources: 2) Avcodes: Airport code database, from which other airports, that are not served by Swedavia, are obtained. 3) Wikipedia. Finally, the listed airports are checked against Wikipedia, to verify if any airports have been missed through the other sources. This selection gave us 186 airports in total.
2023 January
- Nordic Region
- Transport
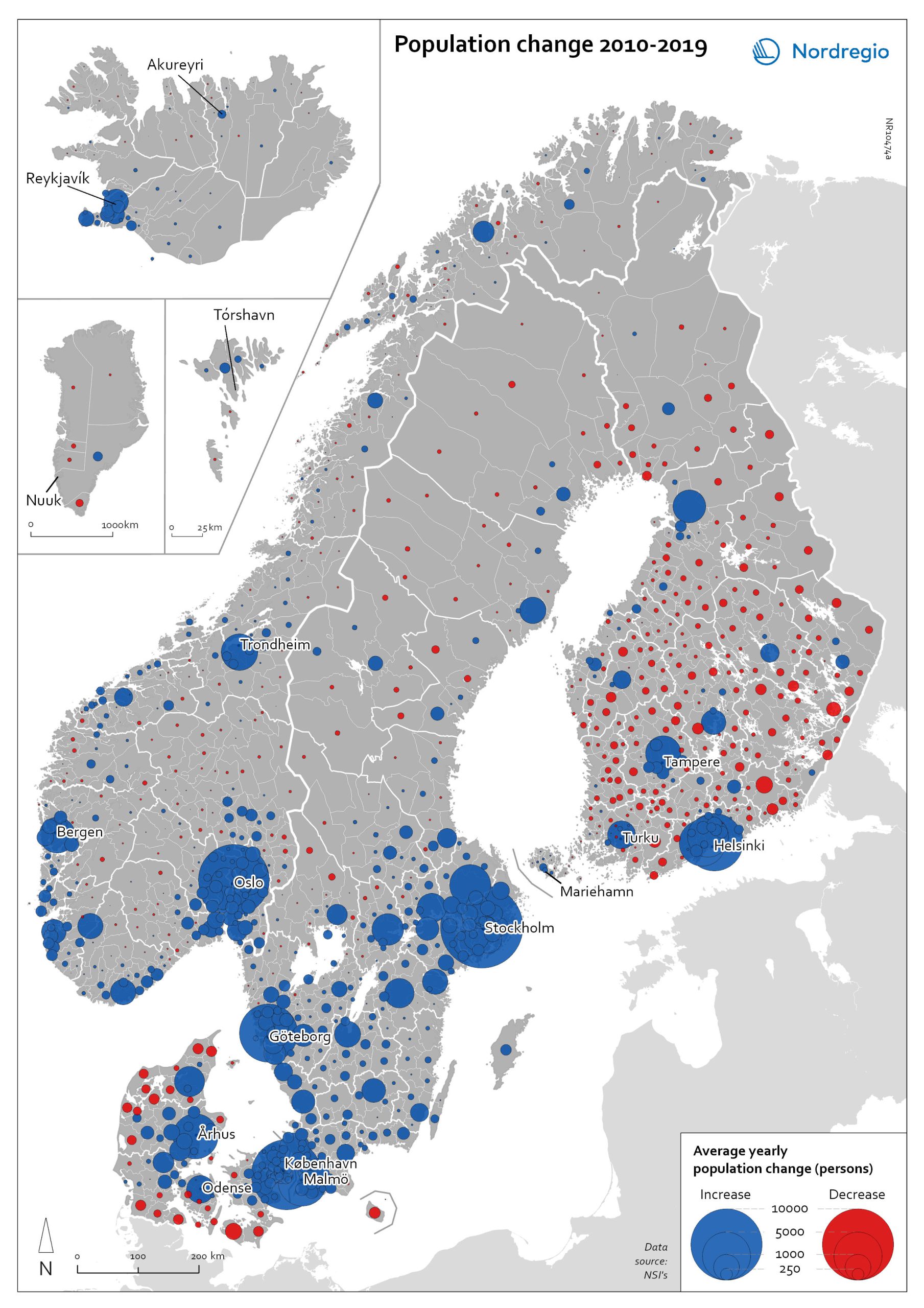
Population change 2010-2019
The map shows the type (positive or negative) and size of population change from 2010 to 2019 in all nordic municipalities. In Finland, Denmark, and Greenland there is a clear pattern of population growth in and around the larger cities and population decline in rural areas. Geographical and administrative differences mean that a much larger number of rural municipalities in Finland are dealing with population decline. Sweden experienced substantial population growth between 2010 and 2019, primarily due to high levels of international immigration. As a result, many rural areas also experienced population growth, particularly in the south of Sweden. However, in the more sparsely populated municipalities in the north of Sweden, the pattern is somewhat similar to that observed in Denmark and Finland, albeit with population decline in lower absolute numbers. Both Iceland and the Faroe Islands experienced substantial growth of their tourism industries within the period. This enabled some rural areas to maintain or even grow their populations. Norway exhibits more balanced population development in general, with a mix of population growth and decline in rural areas throughout the country.
2022 May
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
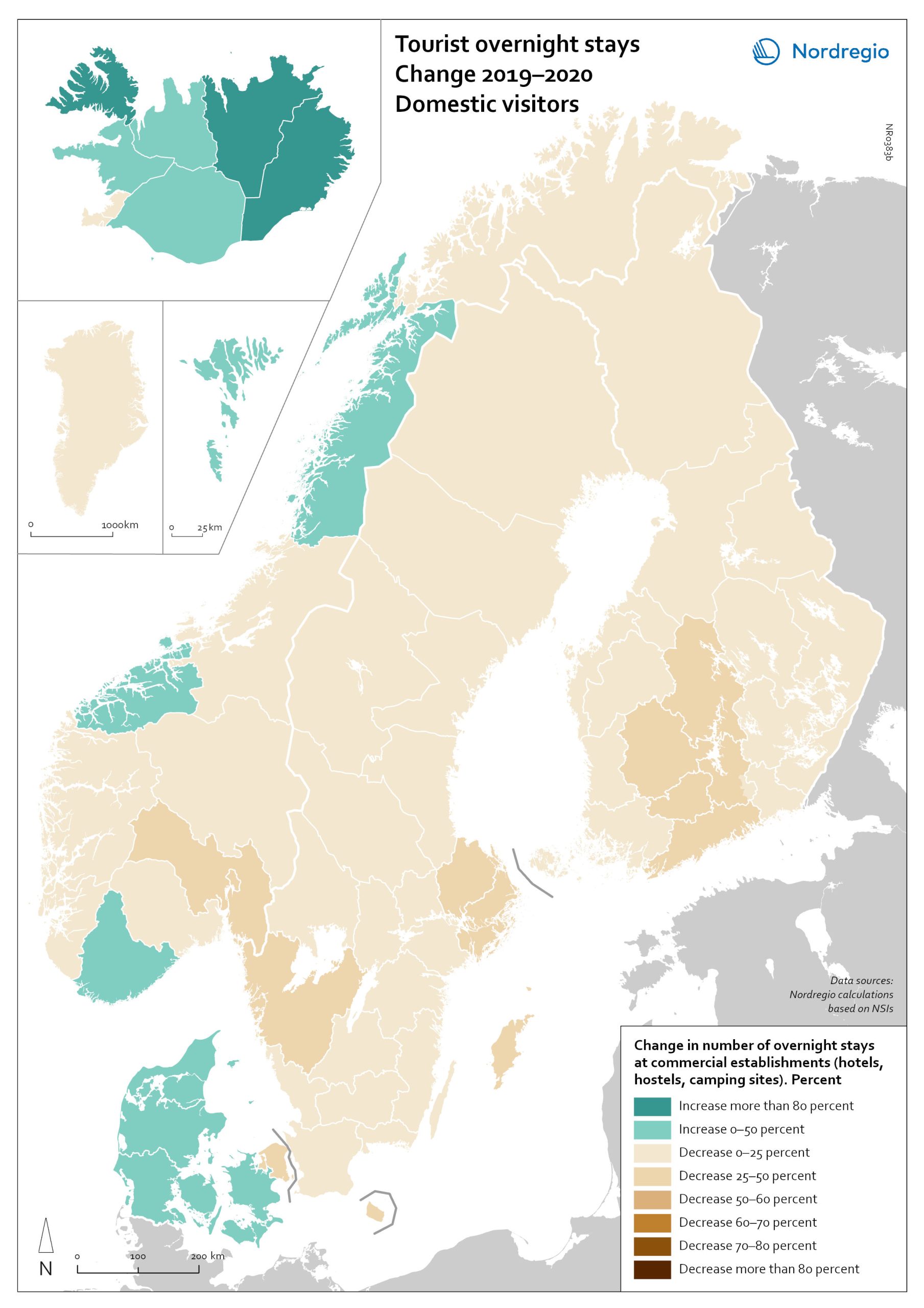
Change in overnight stays for domestic visitors 2019–2020
The map shows the relative change in the number of overnight stays at the regional level between 2019 and 2020 for domestic visitors. This map is related to the same map showing change in overnight stays for foreign visitors 2019–2020. The sharpest fall in visitors from abroad was in destinations where foreign tourists usually make up a high proportion of the total visitors. This is particularly relevant to islands like Åland (89% decrease on foreign visitors, from early 2019 to mid-2020) and to Iceland (66-77% drop depending on region). Lofoten and Nordland County in Norway, as well as Western Norway with Møre and Romsdal, which also have a high proportion of international tourists during the summer season due to their scenic landscape, also recorded sharp falls of 77-79% on foreign visitors during the same period. In Finland, the lake district (South Savo) and Southern Karelia, as well as the coastal Central Ostrobothnia (major cities Vasa and Karleby), recorded a 75-77% drop in the number of visitors from abroad. The fall here was mainly due to the lack of tourists from Russia. Even Finnish Lapland suffered a major fall in international visits during the winter peak period. For many local businesses that rely heavily on winter holidaymakers, the 2021/22 winter was a make-or-break season. In Sweden, the regions of Kalmar, Västra Götaland, Värmland and Örebro lost 77–79% of visitors from abroad, probably due to much fewer visitors from neighbouring Norway and from Denmark. In Denmark, the number of overnight stays by visitors from abroad to the Capital Region was down by 73%, whereas the number of domestic visitors declined by 27%. No region lost as many overnight visitors, both from abroad and domestic, as the capital cities and larger urban areas in the Nordic countries. Copenhagen, Oslo, Stockholm, Helsinki and Reykjavik…
2022 March
- Nordic Region
- Tourism
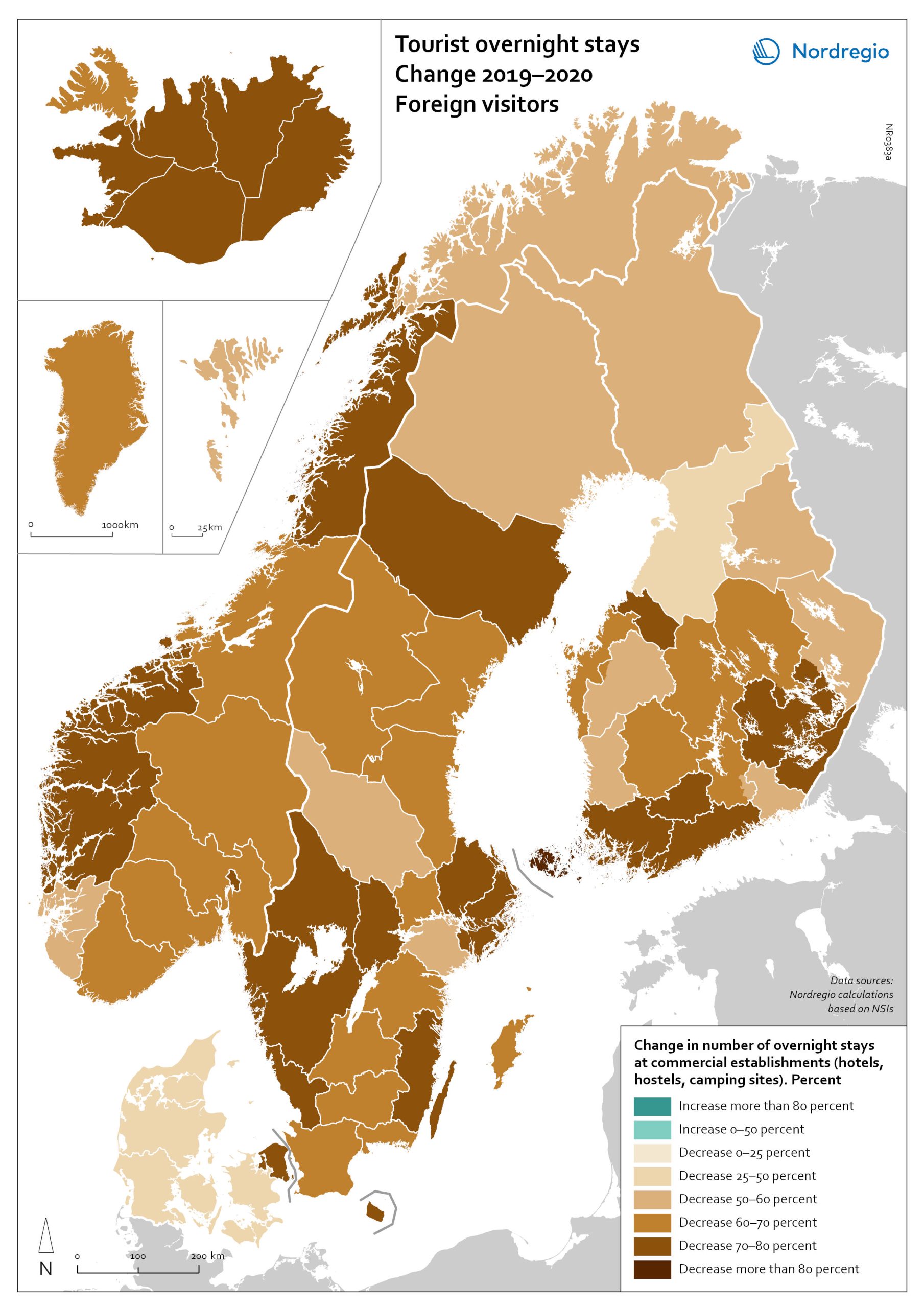
Change in overnight stays for foreign visitors 2019–2020
The map shows the relative change in the number of overnight stays at the regional level between 2019 and 2020 for foreign visitors. This map is related to the same map showing change in overnight stays for domestic visitors 2019–2020. The sharpest fall in visitors from abroad was in destinations where foreign tourists usually make up a high proportion of the total visitors. This is particularly relevant to islands like Åland (89% decrease on foreign visitors, from early 2019 to mid-2020) and to Iceland (66-77% drop depending on region). Lofoten and Nordland County in Norway, as well as Western Norway with Møre and Romsdal, which also have a high proportion of international tourists during the summer season due to their scenic landscape, also recorded sharp falls of 77-79% on foreign visitors during the same period. In Finland, the lake district (South Savo) and Southern Karelia, as well as the coastal Central Ostrobothnia (major cities Vasa and Karleby), recorded a 75-77% drop in the number of visitors from abroad. The fall here was mainly due to the lack of tourists from Russia. Even Finnish Lapland suffered a major fall in international visits during the winter peak period. For many local businesses that rely heavily on winter holidaymakers, the 2021/22 winter was a make-or-break season. In Sweden, the regions of Kalmar, Västra Götaland, Värmland and Örebro lost 77–79% of visitors from abroad, probably due to much fewer visitors from neighbouring Norway and from Denmark. In Denmark, the number of overnight stays by visitors from abroad to the Capital Region was down by 73%, whereas the number of domestic visitors declined by 27%. No region lost as many overnight visitors, both from abroad and domestic, as the capital cities and larger urban areas in the Nordic countries. Copenhagen, Oslo, Stockholm, Helsinki and Reykjavik…
2022 March
- Nordic Region
- Tourism
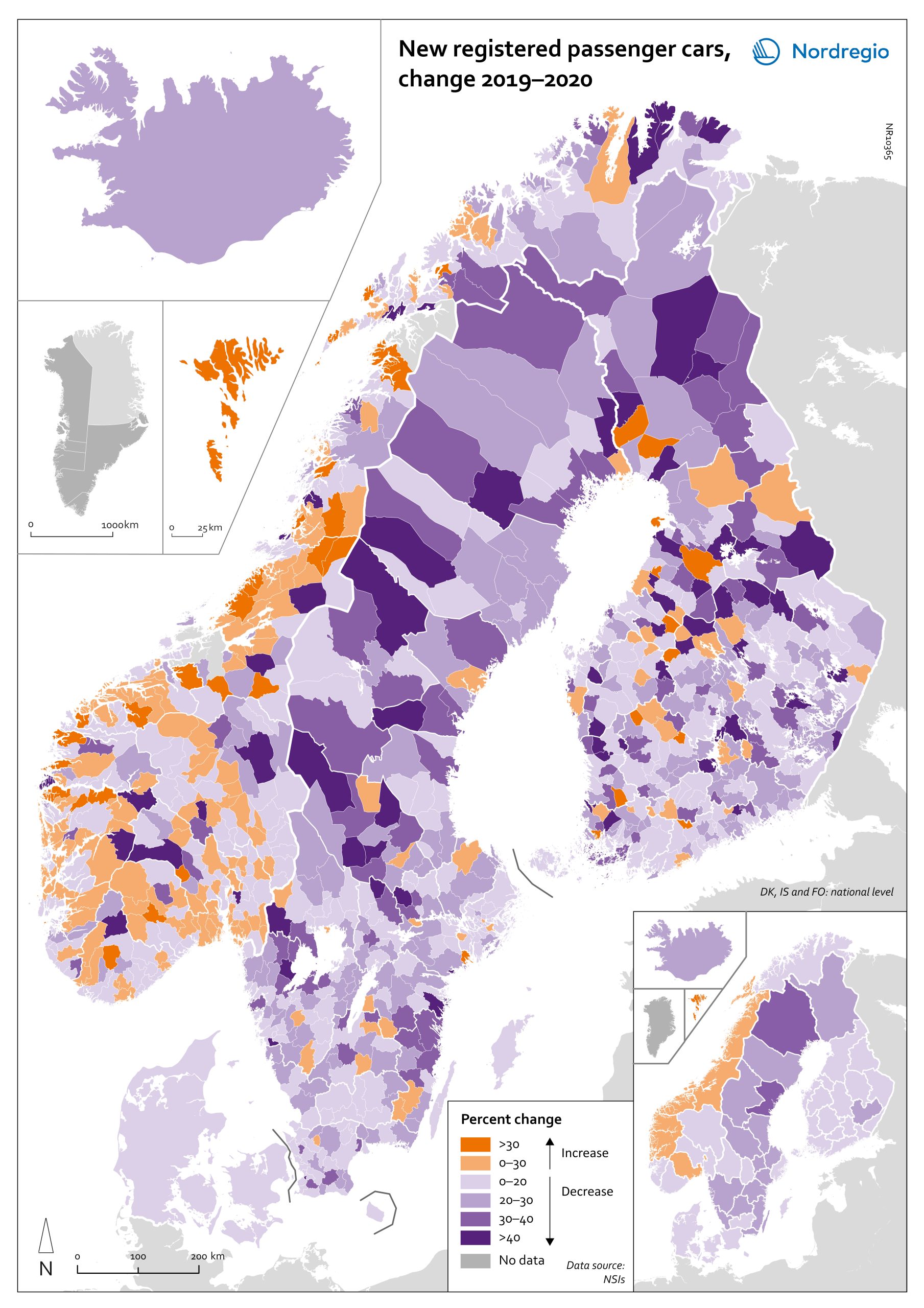
Change in new registered cars 2019-2020
The map shows the change in new registered passenger cars from 2019 to 2020. In most countries, the number of car registrations fell in 2020 compared to 2019. On a global scale, it is estimated that sales of motor vehicles fell by 14%. In the EU, passenger car registrations during the first three quarters of 2020 dropped by 28.8%. The recovery of consumption during Q4 2020 brought the total contraction for the year down to 23.7%, or 3 million fewer cars sold than in 2019. In the Nordic countries, consumer behaviour was consistent overall with the EU and the rest of the world. However, Iceland, Sweden, Finland, Åland, and Denmark recorded falls of 22%–11% – a far more severe decline than Norway, where the market only fell by 2.0%. The Faroe Islands was the only Nordic country to record more car registrations, up 15.8% in 2020 compared to 2019. In Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, there were differences in car registrations in different parts of the country. In Sweden and Finland, the position was more or less the same in the whole of the country, with only a few municipalities sticking out. In Finland and Sweden, net increases in car registrations were concentrated in rural areas, while in major urban areas, such as Uusimaa-Nyland in Finland and Västra Götaland and Stockholm in Sweden, car sales fell between 10%–22%. Net increases in Norway were recorded in many municipalities throughout the whole country in 2020 compared to 2019.
2022 March
- Economy
- Nordic Region
- Transport
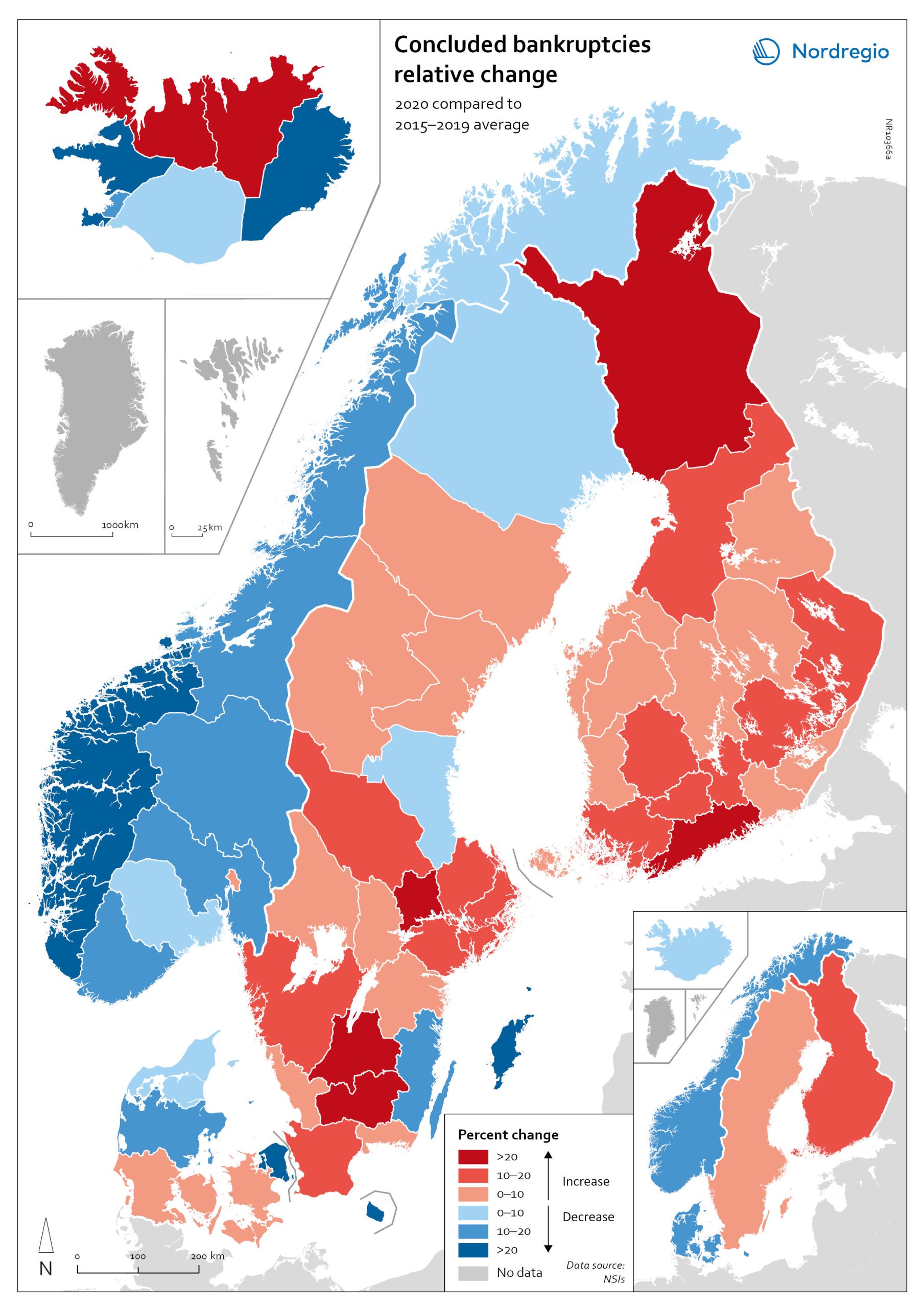
Relative change in the number of business bankruptcies
The map shows the relative change in the number of concluded business bankruptcies by region, 2015–2019 average compared to 2020. At sub-national levels, the distribution of business bankruptcies does not show a clear territorial pattern. In Iceland and Denmark, businesses in the most urbanised areas, including the capital regions, seem to have been those that benefited most from the economic mitigation measures (-23.9% in Höfuðborgarsvæðið and -24.4% in Region Hovedstaden). By contrast, Oslo is the only Norwegian region where there were more business bankruptcies in 2020 compared to the 2015–2019 baseline (1.9% increase). Most Norwegian regions did, in fact, have fewer bankruptcies in 2020, particularly in the western regions. One plausible explanation for this could be that the number of business failures during the baseline period was especially high in western Norway due to the fall in oil prices in 2014–2015. In Sweden the situation is even more mixed. Here, businesses in urban areas seem to have been more exposed to the distress caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. The most urbanised regions in the Stockholm-Gothenburg-Malmö corridor registered a greater increase in liquidations (Jönköping, Kronoberg and Södermanland regions saw surges of around 20%). However, predominantly rural regions in Sweden, such as Västerbotten and Jämtland, also recorded higher numbers of bankruptcies than average (9.8% and 8.8% increase, respectively). In Finland, the impact was greater in Lapland (26.9%) and around Helsinki (Uusimaa, 25.9%) than in the central parts of the country. Åland also experienced a moderate rise in business bankruptcies in 2020 (4.0%), mostly related to the tourism sector.
2022 March
- Economy
- Nordic Region
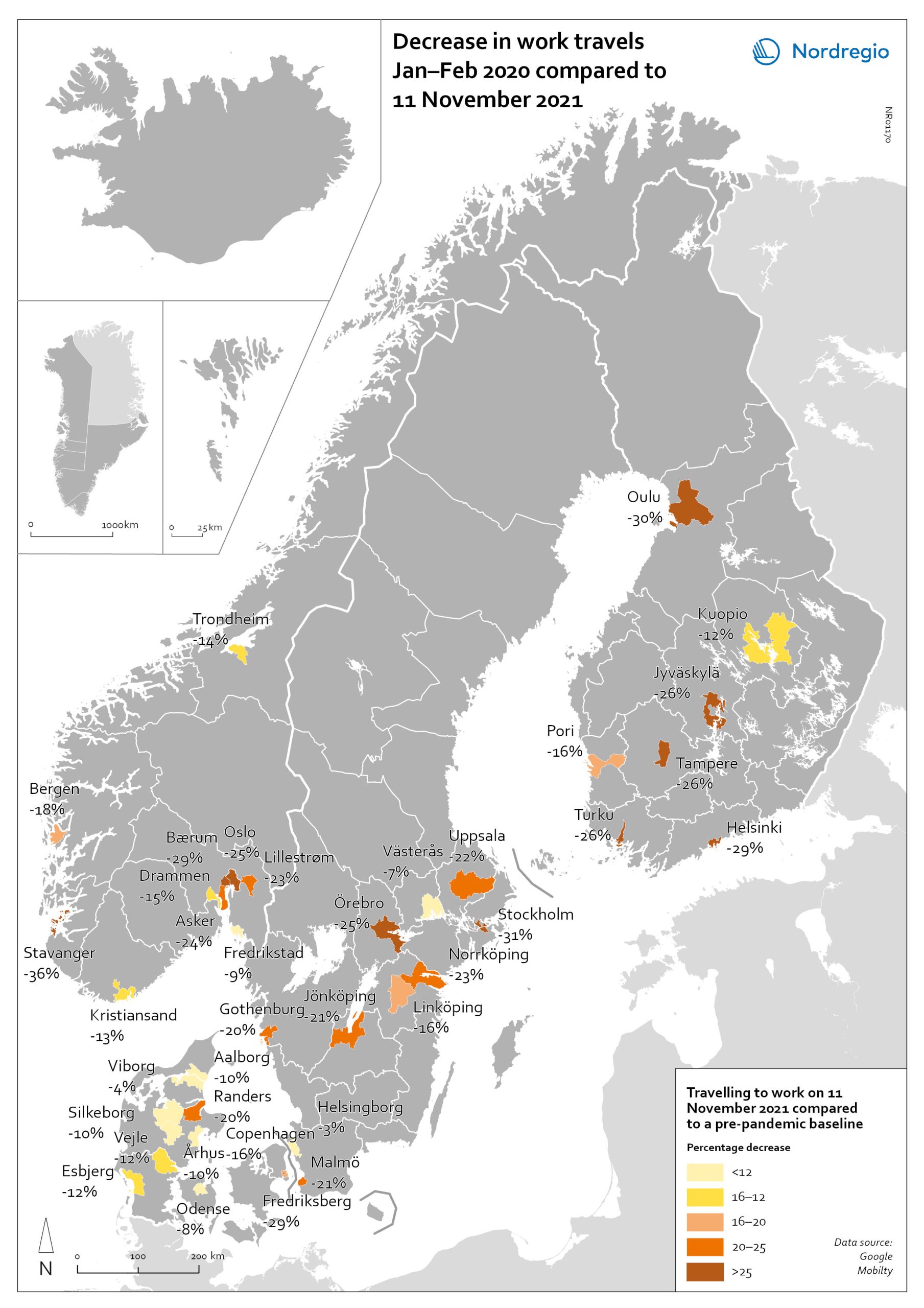
Change in work travels Jan-Feb 2020 compared to Nov 2021
The map shows changes in number of people travelling to work in the Nordic municipalities with the biggest populations comparing November 2021 to a pre-pandemic baseline. The map compares the average number of people who travelled to work on a weekday in January and February 2020 with the number of people who travelled to work on 11 November 2021 in the ten largest cities of Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden. The date was selected as the reference date as it is considered to be a relatively typical Thursday. It also represents a point when few movement restrictions were in place in the Nordic countries. As can be seen from the map, all of the municipalities highlighted recorded a fall in work-related travel on 11 November compared to the pre-pandemic baseline. It was biggest in Stavanger (-36%), followed by Stockholm (-31%), Oulu (-30%), Bærum (adjacent to Oslo) (-29%), Frederiksberg (adjacent to Copenhagen) (-29%) and Helsinki (-29%). In general, the decrease was highest around the capital regions and larger cities, but there were exceptions, for example, Jyväskylä (-26%), Örebro (-25%), Jönköping (-21%), and Randers (-20%). Several large municipalities also stood out because their patterns did not change so much, for example, Helsingborg (-3%) and Västerås (-7%) in Sweden; Viborg (-3%) and Odense (-8%) in Denmark.
2022 March
- Labour force
- Nordic Region
- Transport
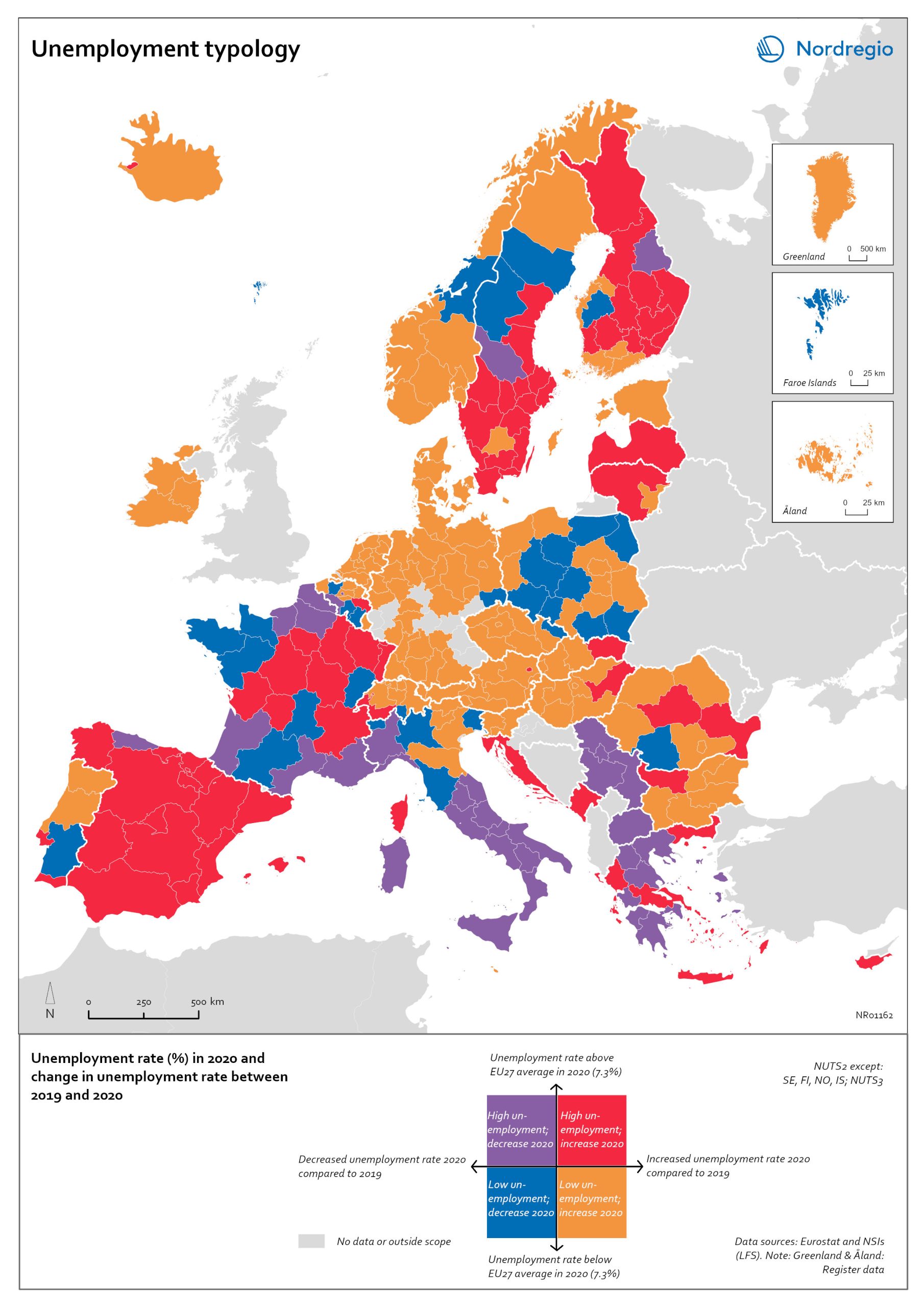
Unemployment typology
The map shows a typology of European regions by combining information on pre-pandemic unemployment rates with unemployment rates in 2020, based on the annual Labour Force Survey (LFS) that is measured in November. On one axis, the typology considers the extent of the change in the unemployment rate between 2019 and 2020. On the other axis, it considers whether the unemployment rate in 2020 was above or below the EU average of 7.3%. Regions are divided into four types based on whether the unemployment rate decreased or increased and how it relates to the EU average. Regions falling into the first type, shown in red on the map, had an increase in the unemployment rate in 2020 as well as an above-average unemployment rate in general in 2020. These regions were most affected by the pandemic. They are mainly found in northern and central parts of Finland, southern and eastern Sweden, the capital area of Iceland, Latvia, Lithuania, Spain and central parts of France. Regions falling into the second type, shown in orange on the map, had an increase in the unemployment rate in 2020 but a below-average unemployment rate in general in 2020. These regions had low pre-pandemic unemployment rates and so were not as badly affected as the red regions, despite the rising unemployment rates. They are located in Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Åland, southern and western Finland, Sweden (Gotland, Jönköping, and Norrbotten), Estonia, Ireland, northern Portugal and central and eastern parts of Europe.
2022 March
- Europe
- Labour force
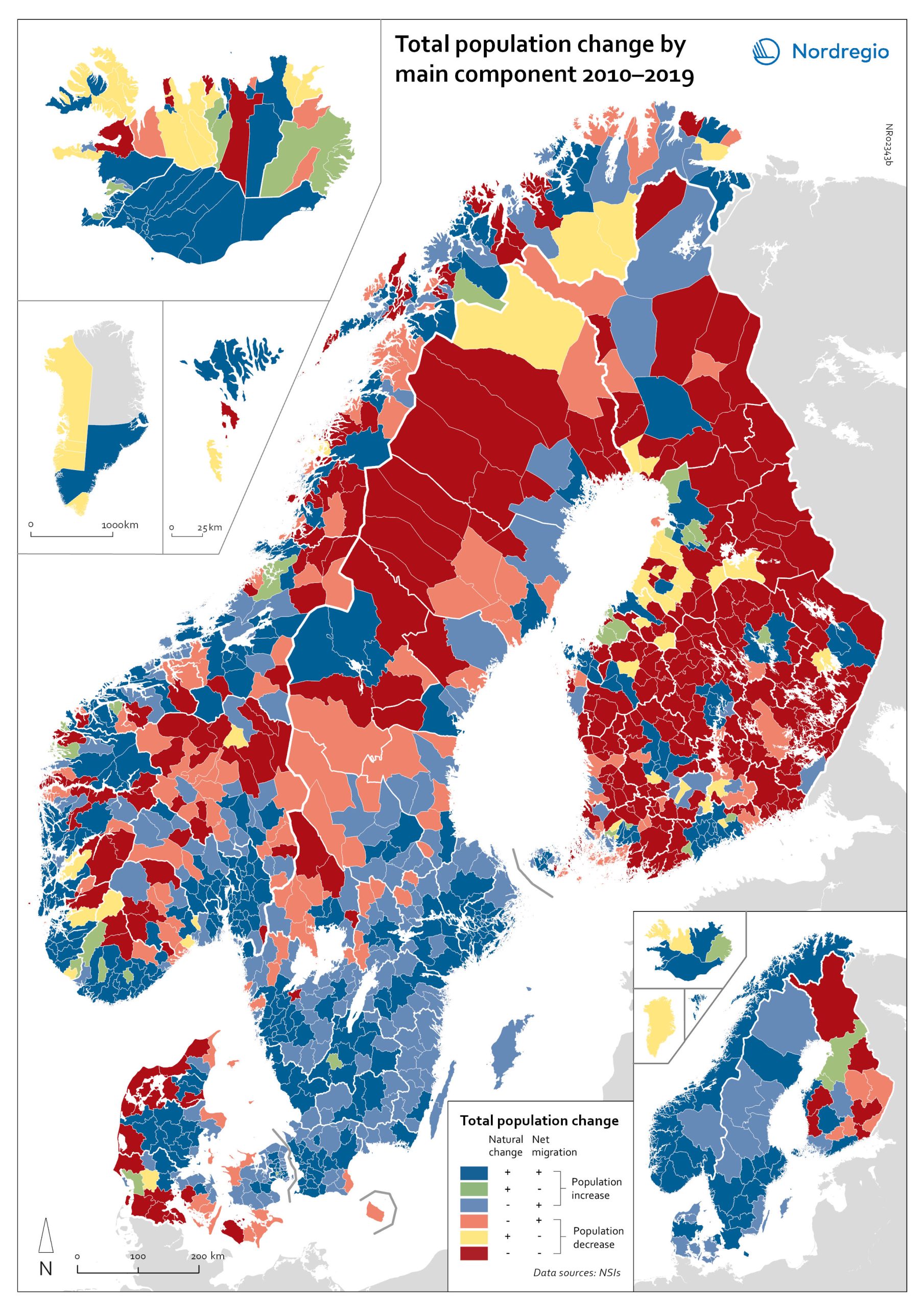
Population change by component 2010-2019
The map shows the population change by component 2010-2019. The map is related to the same map showing regional and municipal patterns in population change by component in 2020. Regions are divided into six classes of population change. Those in shades of blue or green are where the population has increased, and those in shades of red or yellow are where the population has declined. At the regional level (see small inset map), all in Denmark, all in the Faroes, most in southern Norway, southern Sweden, all but one in Iceland, all of Greenland, and a few around the capital in Helsinki had population increases in 2010-2019. Most regions in the north of Norway, Sweden, and Finland had population declines in 2010-2019. Many other regions in southern and eastern Finland also had population declines in 2010-2019, mainly because the country had more deaths than births, a trend that pre-dated the pandemic. In 2020, there were many more regions in red where populations were declining due to both natural decrease and net out-migration. At the municipal level, a more varied pattern emerges, with municipalities having quite different trends than the regions of which they form part. Many regions in western Denmark are declining because of negative natural change and outmigration. Many smaller municipalities in Norway and Sweden saw population decline from both negative natural increase and out-migration despite their regions increasing their populations. Many smaller municipalities in Finland outside the three big cities of Helsinki, Turku, and Tampere also saw population decline from both components. A similar pattern took place at the municipal level in 2020 of there being many more regions in red than in the previous decade.
2022 March
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
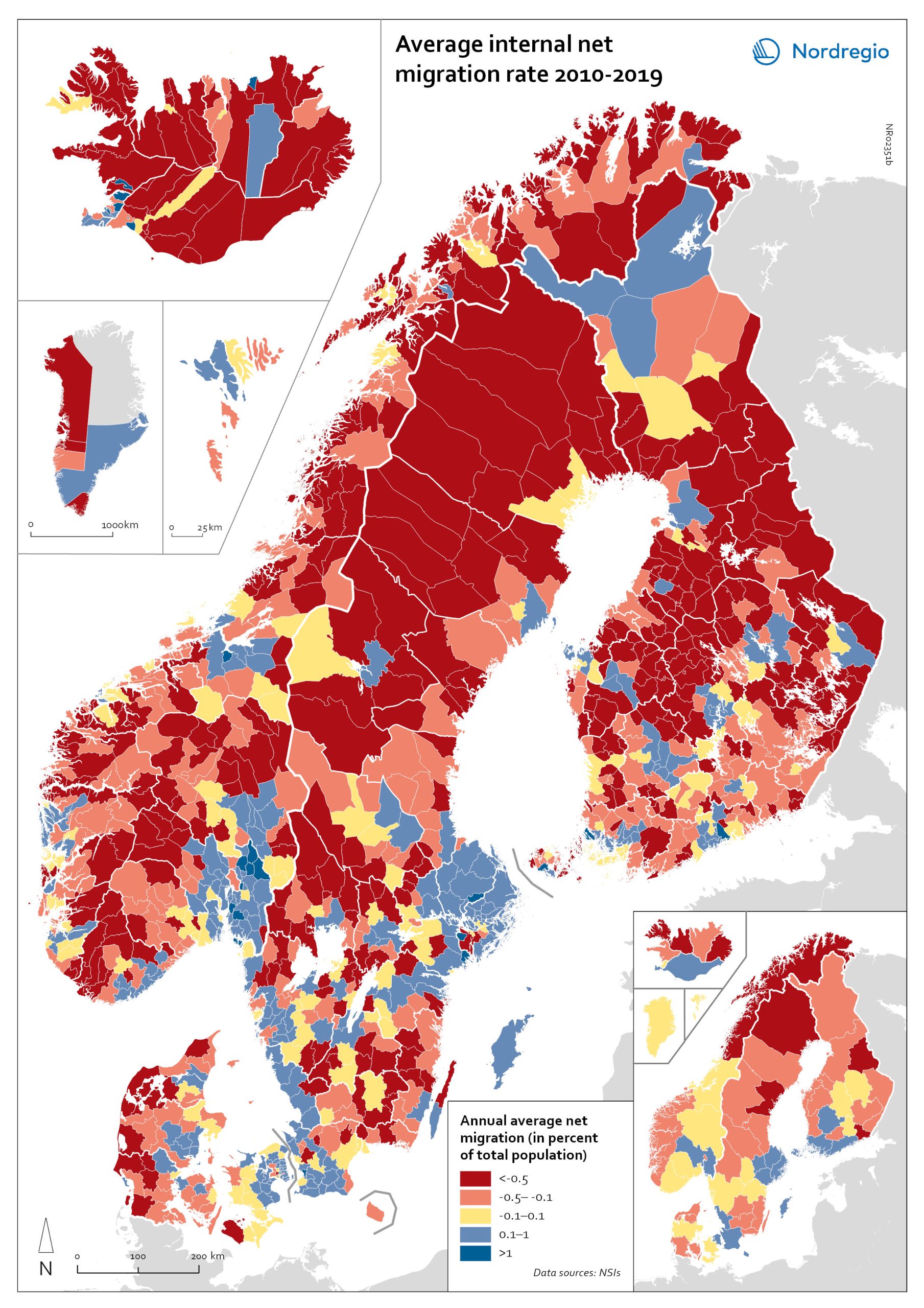
Net internal migration rate, 2010-2019
The map shows the annual average internal net migration in 2010-2019. The map is related to the same map showing net internal migration in 2020. The maps show several interesting patterns, suggesting that there may be an increasing trend towards urban-to-rural countermigration in all the five Nordic countries because of the pandemic. In other words, there are several rural municipalities – both in sparsely populated areas and areas close to major cities – that have experienced considerable increases in internal net migration. In Finland, for instance, there are several municipalities in Lapland that attracted return migrants to a considerable degree in 2020 (e.g., Kolari, Salla, and Savukoski). Swedish municipalities with increasing internal net migration include municipalities in both remote rural regions (e.g., Åre) and municipalities in the vicinity of major cities (e.g., Trosa, Upplands-Bro, Lekeberg, and Österåker). In Iceland, there are several remote municipalities that have experienced a rapid transformation from a strong outflow to an inflow of internal migration (e.g., Ásahreppur, Tálknafjarðarhreppurand, and Fljótsdalshreppur). In Denmark and Norway, there are also several rural municipalities with increasing internal net migration (e.g., Christiansø in Denmark), even if the patterns are somewhat more restrained compared to the other Nordic countries. Interestingly, several municipalities in capital regions are experiencing a steep decrease in internal migration (e.g., Helsinki, Espoo, Copenhagen and Stockholm). At regional level, such decreases are noted in the capital regions of Copenhagen, Reykjavík and Stockholm. At the same time, the rural regions of Jämtland, Kalmar, Sjælland, Nordjylland, Norðurland vestra, Norðurland eystra and Kainuu recorded increases in internal net migration. While some of the evolving patterns of counterurbanisation were noted before 2020 for the 30–40 age group, these trends seem to have been strengthened by the pandemic. In addition to return migration, there may be a larger share of young adults who…
2022 March
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region
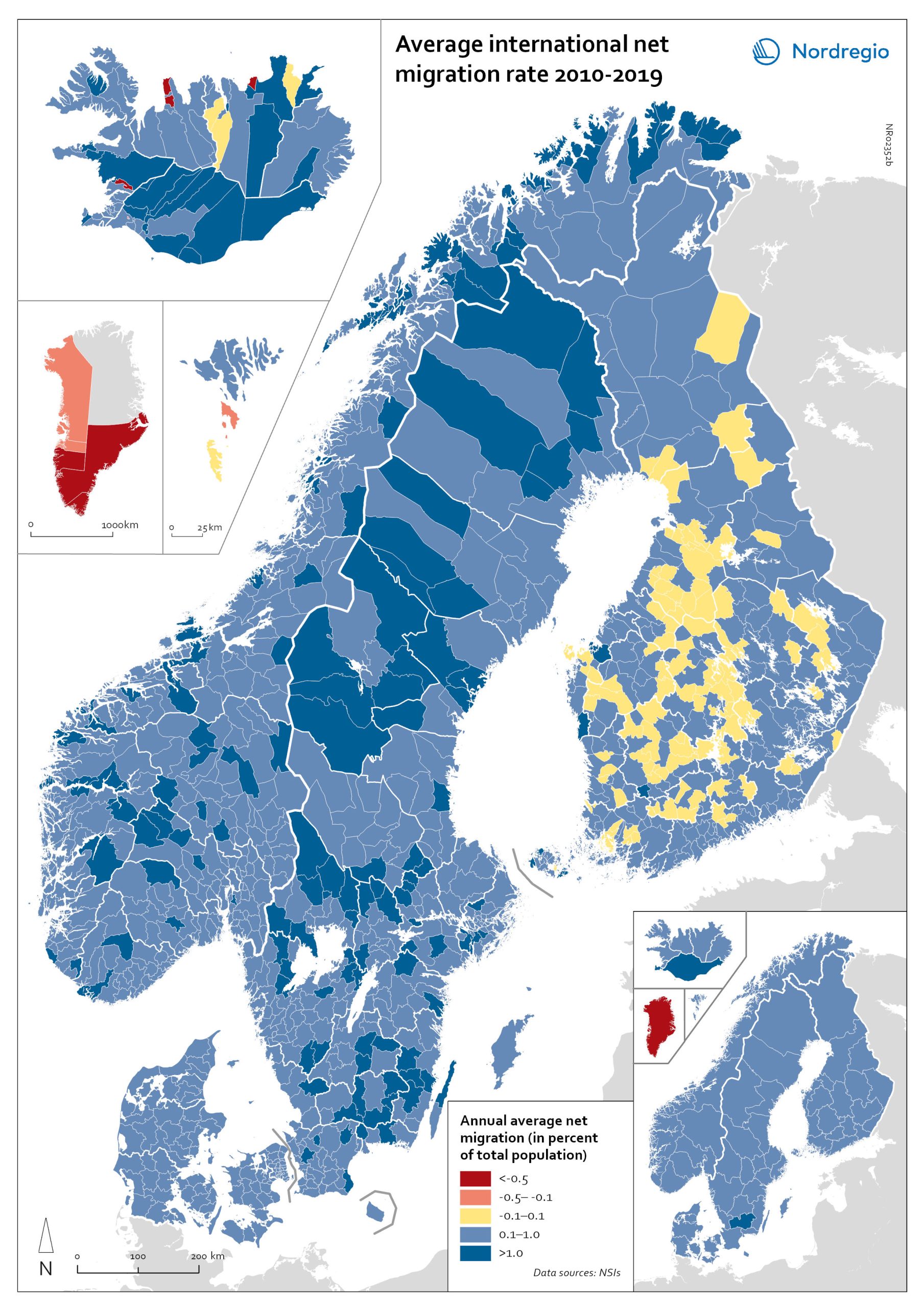
Net international migration rate, 2010–2019
The map shows the annual average international net migration from 2010 to 2019. The map is related to the same map showing net migration in 2020. At regional level, there are only minor changes between the net migration in 2010-2019 and 2020. All regions of Norway, all regions of Sweden except Gotland and Uppsala, and the regions of Österbotten in Finland, Midtjylland in Denmark and Norðurland eystra in Iceland experienced a slight decrease in international net migration I 2020 compared to 2010-2019. There is a more marked increase in net migration in the Faroe Islands, Greenland and the region of Norðurland vestra in Iceland, and a slight increase in the region of Austurland in Iceland. At municipal level, the maps show more changing patterns. In Denmark, Norway and Sweden, several municipalities – both in the capital, intermediate, and rural regions – had lower levels of international net migration in 2020 compared to 2010-2019. In Iceland and Finland, the picture is more balanced, with some municipalities showing a decrease, others an increase. In the Faroe Islands and Greenland, several municipalities/regions had an increase in international net migration.
2022 March
- Demography
- Migration
- Nordic Region

