82 Maps
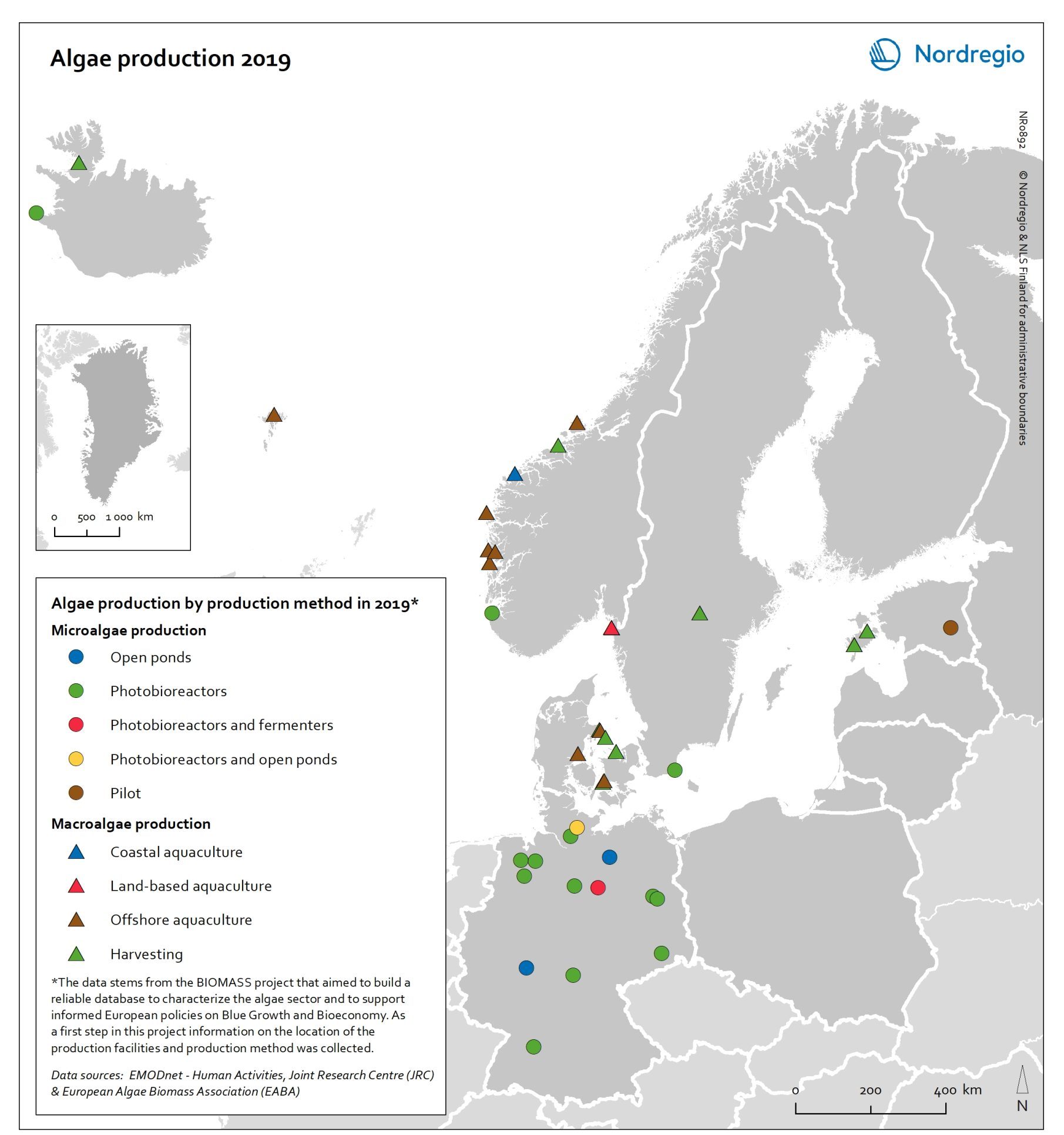
Algae production in 2019
This map shows location of algae production by production method in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region in 2019 Algae and seaweeds are gaining attention as useful inputs for industries as diverse as energy and human food production. Aquatic vegetation – both in the seas and in freshwater – can grow at several times the pace of terrestrial plants, and the high natural oil content of some algae makes them ideal for producing a variety of products, from cosmetic oils to biofuels. At the same time, algae farming has added value in potential synergies with farming on land, as algae farms utilise nutrient run-off and reduce eutrophication. In addition, aquatic vegetation is a highly versatile feedstock. Algae and seaweed thrive in challenging and varied conditions and can be transformed into products ranging from fuel, feeds, fertiliser, and chemicals, to third-generation sugar and biomass. These benefits are the basis for seaweed and algae emerging as one of the most important bioeconomy trends in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea region. The production of algae for food and industrial uses has hence significant potential, particularly in terms of environmental impact, but it is still at an early stage. The production of algae (both micro- and macroalgae) can take numerous forms, as shown by this map. At least nine different production methods were identified in the region covered in this analysis. A total of 41 production sites were operating in Denmark, Estonia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Norway, Germany, and Sweden. Germany has by far the most sites for microalgae production, whereas Denmark and Norway have the most macroalgae sites.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Others
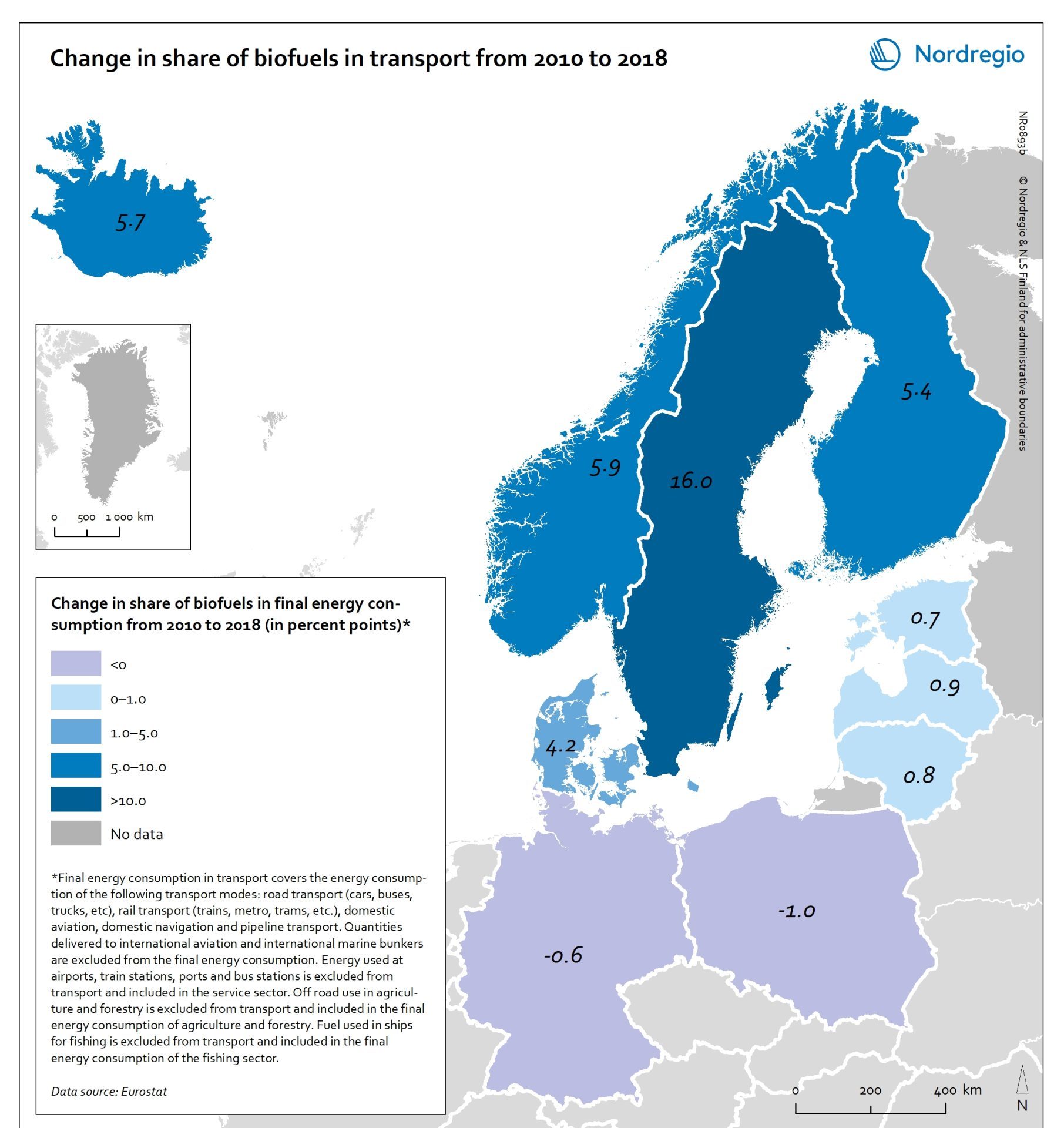
Change in share of biofuels in transport from 2010 to 2018
This map shows change in share of biofuels in final energy consumption in transport in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region from 2010 to 2018. Even though a target for greater use of biofuels has been EU policy since the Renewable Energy and Fuel Quality Directives of 2009, development has been slow. The darker shades of blue on the map represent higher increase, and the lighter shades of blue reflect lower increase. The lilac color represent decrease. The Baltic Sea represents a divide in the region, with countries to the north and west experiencing growth in the use of biofuels for transport in recent years. Sweden stands out (16 per cent growth), while the other Nordic countries has experienced more modest increase. In the southern and eastern parts of the region, the use of biofuels for transport has largely stagnated. Total biofuel consumption for transport has risen more than the figure indicates due to an increase in transport use over the period.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Transport
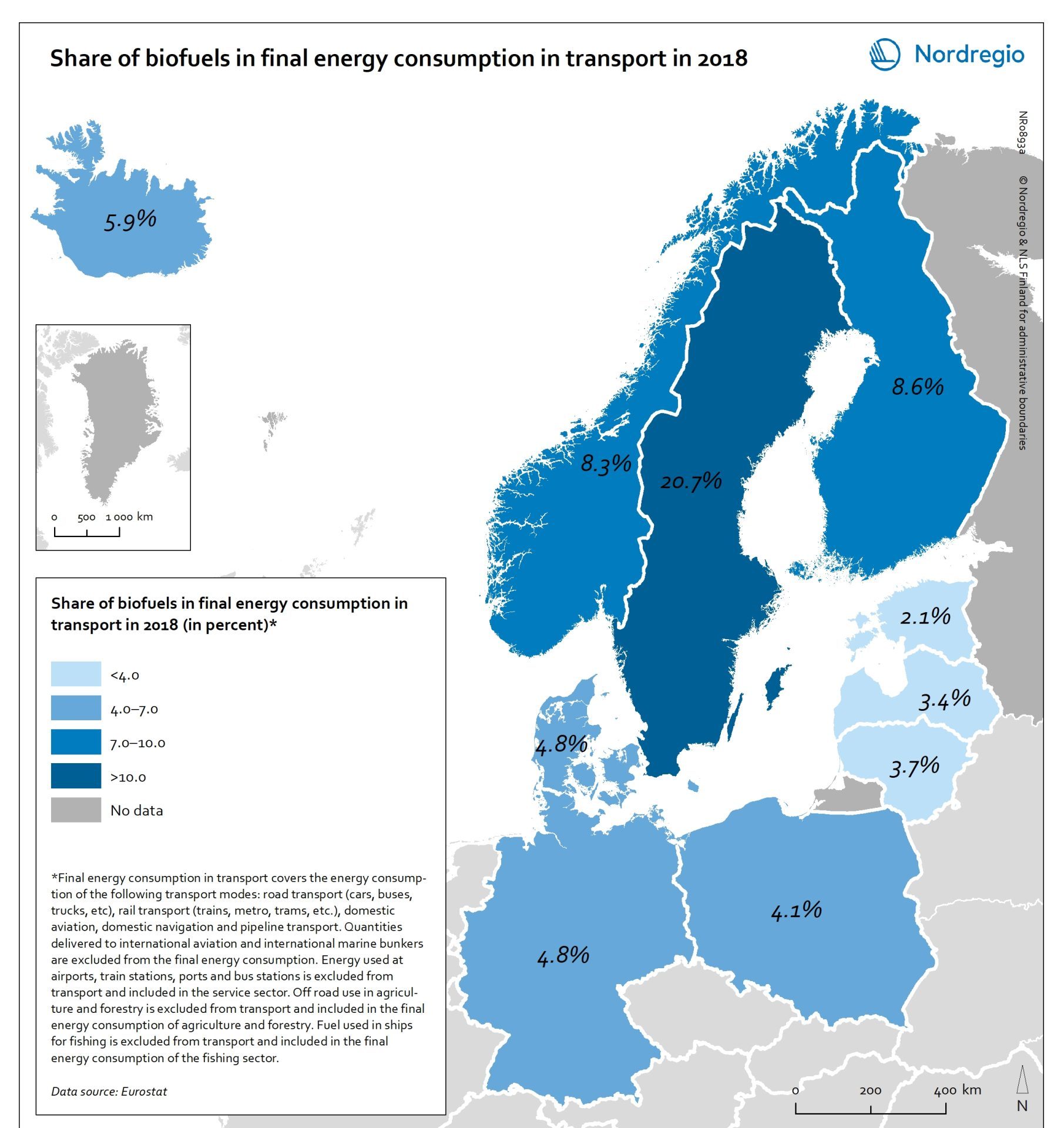
Share of biofuels in transport in 2018
This map shows the share of biofuels in final energy consumption in transport in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region in 2018. There has been considerable political support for biofuels and in the EU, this debate has been driven by the aim of reducing dependency on imported fuels. For instance, 10 per cent of transport fuel should be produced from renewable sources. The darker shades on the map represent higher proportions, and the lighter shades reflect lower proportions. As presented by the map, only Sweden (20.7%) had reached the 10 per cent target in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Region in 2018. Both Finland (8.3%) and Norway (8.3%) were close by the target, while the other countries in the region were still lagging behind, particularly the Baltic countries.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Transport
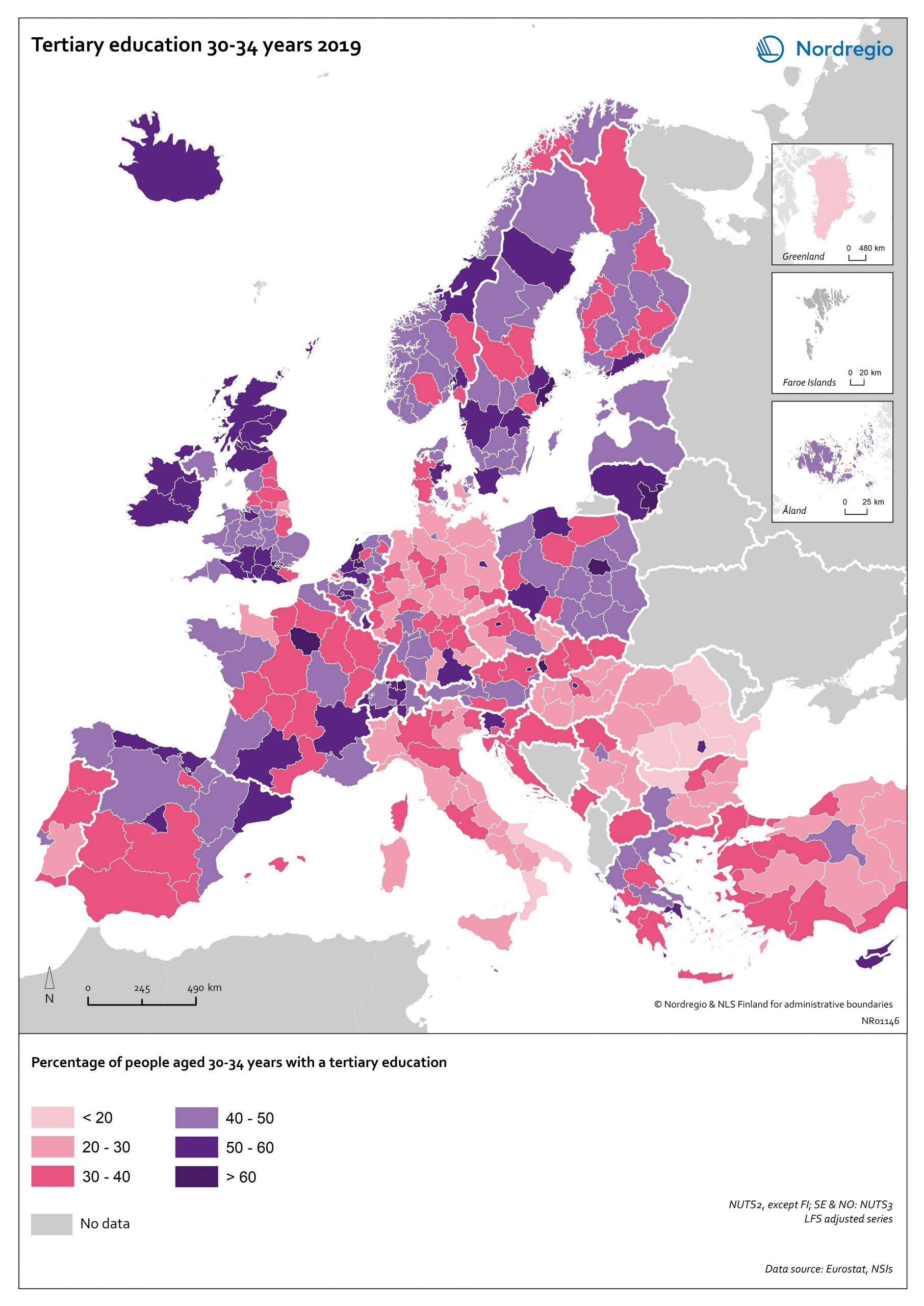
Tertiary education attainment level of 30- to 34-year-olds 2019
The map shows the proportion of the population aged 30-34 years old, who had a tertiary education at the European level in 2019. Purple shades indicate higher proportions, and pinkish shades reflect lower proportions. It is common to show the education attainment for the age group 30-34 since it is an age group where most people have finalised their studies. The focus on this age group makes it easier to see recent trends and outcomes of policies. Overall, over 40% of Europeans aged 30-34 years old had a tertiary education in 2019. Young people in the Nordic countries are among the most educated, with approximately half of 30 to 34-year-olds achieving a tertiary education across all Nordic countries. The highest proportions can be found in the capital regions. Stockholm is particularly noteworthy, with over 60% of 30 to 34-year-olds having had a tertiary education. Regions with prominent universities also stand out – for example, Skåne, Uppsala, Västerbotten and Västra Götaland (Sweden), Trøndelag (Norway) and Østjylland (Denmark).
2020 October
- Baltic Sea Region
- Demography
- Europe
- Nordic Region
- Others
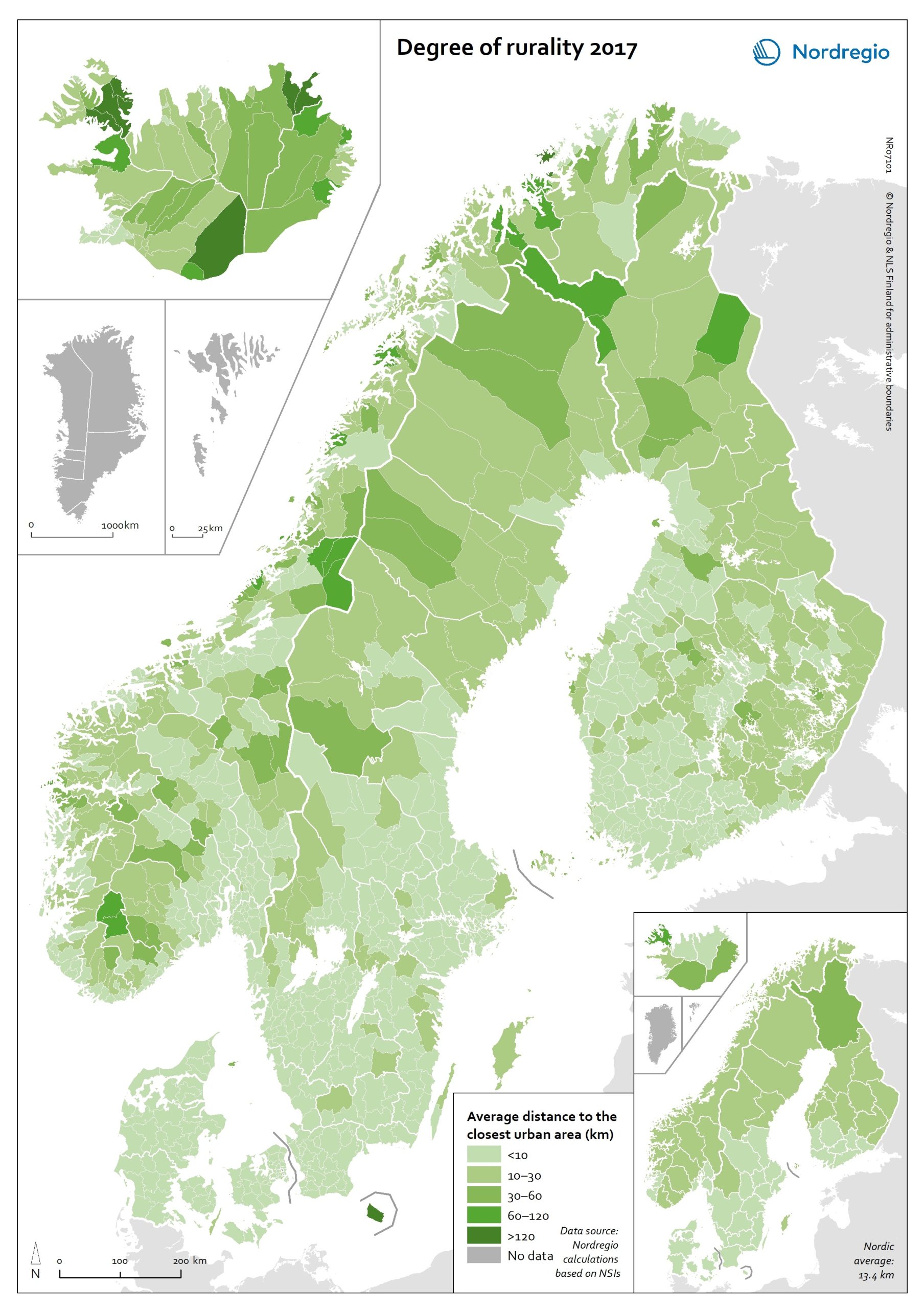
Degree of rurality at the municipal and regional level in 2017
This map shows the average distance to the edge of the closest urban area for the population living outside urban areas in the Nordic municipalities and regions. These figures are of particular interest in the analysis of urban-rural patterns and the Nordic populations’ access to local services in sparsely population areas. The darker shades on the map indicate longer average distances to the edge of the nearest urban area, and the lighter shades indicate shorter average distances. While almost all Danish municipalities have an average distance of below 10 km from rural grid cells to the nearest urban area, a large share of the municipal populations of the remaining Nordic countries need to contend with longer average distances to local services. The largest distances can be found in several municipalities of Iceland and Norway (Árneshreppur 230 km, Hasvik 154 km), whereas the largest average distances for Finnish and Swedish municipalities are considerably shorter (Enontekiö 103 km, Storuman 52 km). Regarding within-country variation, shorter average distances can generally be found in southwestern Finland and southern Sweden, in comparison with the more remote parts of these countries. Both Norway and Iceland provide a rather more mixed picture, since there are municipalities with shorter average distances scattered across different parts of each country. Method used to calculate the degree of rurality In order to take into account access to services such as grocery stores, pharmacies, schools, community centres and public transport, the European definition of urban grid cells was used to create this map, i.e. a population density threshold of 300 inhabitants per km2 applied to grid cells of 1 km2. The closest distance was calculated from each rural grid cell centroid to the nearest urban grid cell centroid along the existing road network traversable by car, including car ferries, based on population…
2020 October
- Environment
- Nordic Region

Settlements on permafrost in the Arctic
The map shows the distribution of coastal and inland settlements on permafrost in the Arctic in 2017. Permafrost is ground that is at or below 0°C for at least 2 consecutive years. The purple tones indicate settlements located on permafrost and distinguishes between coastal (light purple) and inland (dark purple) settlements. Settlements located outside the permafrost extent are in yellow. Among all Arctic settlements, 66,1% are located on permafrost. Settlements are classified as permafrost settlements if they are located within the permafrost extent, comprising zones of continuous, discontinuous, sporadic, or isolated permafrost. Among all permafrost settlements 46,0% are coastal. Coastal settlements are defined by their dependency to the sea. They are either adjacent to the coast, located inland along large rivers with a free connection to the open sea, or located within a short distance to the sea (0-200 km). In this map, coastal settlements comprise all settlements that are located within an Arctic subregion adjacent to the coast. Most of the settlements located outside the permafrost extent area are in the Nordic countries (Iceland, Norway, the Faroe Islands, Sweden, and Finland) as well as in the southern part of Alaska (USA) and the western part of the Russian Arctic. Almost all Arctic settlements in the Russian Federation and in Canada are located on permafrost. The increase in air surface temperature observed in the Arctic causes dramatic changes in the permafrost thermal regime leading to the destabilisation of infrastructure built on permafrost.
2019 March
- Arctic
- Demography
- Environment

Land Cover in the Arctic
The terrestrial ecosystem of the Arctic is characterized by low tundra vegetation, composed of shrubs, herbaceous plants, mosses, and lichens. Arctic vegetation is becoming more productive due to increasing air temperature. One of the main trends shows an increase in tall shrub cover. On the contrary, the cover of lichen and moss has declined in response to regional warming.
2019 January
- Arctic
- Environment

Components of the cryosphere in the Arctic
This map shows the main components of the cryosphere in the Arctic: sea-ice, permafrost, ice-sheets, and glaciers. Sea-ice covers most of the Arctic Ocean during winter. The sea-ice extent reaches its maximum in March, when it covers approximately 14-16 million km2. Since 1979, the Arctic ice extent in winter has decreased by 3% per decade relative to the 1981-2010 average, and this trend accelerates. Similarly, ice-sheets and glaciers, which cover globally over 15 million km2 are melting. In the Arctic, the main ice-sheet is the Greenlandic ice sheet. Most of the land surface in the Arctic is underlay by permafrost, ground that is at or below 0°C for at least 2 consecutive years. The purple tones on the map indicates the extent of the northern circumpolar permafrost. Permafrost can occur as continuous (dark purple, 90-100% coverage), discontinuous (purple, 50-90% coverage), sporadic (light purple, 10-50%), or isolated patches (magenta, 0-10% coverage). Permafrost is thawing due to increased air temperatures and precipitations in the Arctic. Permafrost temperature increased by 0.29 ± 0.12°C between 2007 and 2016.
2019 January
- Arctic
- Environment

Protected areas in the Arctic
Within the northern circumpolar permafrost region, there are ca. 1300 protected areas. Most of these areas are terrestrial (1069), while 126 are coastal – defined as partially within the marine environment – and 62 are marine. The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA)[1] includes a wide range of protected areas, including national protected areas recognized by the government, areas designated under regional and international conventions, privately protected areas and indigenous peoples’ and community conserved territories and areas. Greenland is one of the countries with the largest protected terrestrial area (41,0%). [1] IUCN and UNEP-WCMC (2019), The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) [On-line], [January 2019]. Cambridge, UK: UNEP-WCMC. Available at: www.protectedplanet.net.
2019 January
- Arctic
- Environment

Early leavers from education and training 2016
This map shows the percent of early school leavers in the Nordic Region (NUTS 2 level) and Baltic states in 2016, calculated as the total number of individuals aged 18-24 having a lower secondary education as the highest level attained and not being involved in further education or training. The numbers in each region indicate the proportion of females per 100 males. The yellow/red shading indicates the percent of early school leavers in 2016. The lighter the colour the lower the percentage of early school leavers in 2016. The grey colour indicates no data. Early school leaving is of concern in the Nordic Region to varying degrees. From a pan-European perspective, the Danish (7.2%), Swedish (7.4%) and Finnish (7.9%) averages all fall below the EU average (10.7%) and are in line with the Europe 2020 target of below 10%. The Norwegian average (10.9%) remains slightly above the target but is comparable to the EU average. The average rate of early school leaving in Iceland (19.8%) is substantially higher than the other Nordic countries and the EU average. There is both a spatial and a gender dimension to this problem. The spatial dimension of early school leaving is highlighted in this map, which shows rates of early school leaving in the Nordic Region at the NUTS 2 level. The map highlights the comparatively high rates in Norway, particularly in the north. It is worth noting that, although still high in a Nordic comparative perspective, early school leaving rates have decreased in all Norwegian regions since 2012. Rates are also high in Greenland, with a staggering 57.5% of young people aged 18–24 years who are not currently studying and who have lower secondary as their highest level of educational attainment. The map also shows the gender dimension of early school leaving, with…
2018 February
- Baltic Sea Region
- Labour force
- Nordic Region

Gross Regional Product per capita in million PPP 2015
This map shows the gross regional product per capita in million purchasing power parity (PPP) in all Nordic and Baltic Regions in 2015. The green tones indicate regions with a gross regional product per capita above the EU28 average. The darker the tone the higher the gross regional product per capita. The brown/yellow shading indicates regions with a gross regional product per capita below the EU28 average. The darker the tone the lower the gross regional product per capita. In economic development terms, the Nordic Region continues to perform well in relation to the EU average. Urban and capital city regions still show high levels of GDP per capita reflecting the established pattern throughout Europe. Stockholm, Oslo, Helsinki, Copenhagen and the western Norwegian regions are among the wealthiest in Europe, again confirming that the capital regions and larger cities are the strongest economic centres in the Nordic Region. In addition to these urban regions, some others also display high levels of GRP per capita. What is interesting is that in the aftermath of the economic crisis some second-tier city regions, such as Västra Götaland with Gothenburg in Sweden, are now also displaying fast growth rates as indeed are some less metropolitan regions in the western part of Denmark. These regions display GRP per capita levels which correspond to, or even exceed, those of most metropolitan regions in Europe. most of the central and eastern parts of Finland remain below the EU average.
2018 February
- Baltic Sea Region
- Economy

Forest felling average 2013-2015
This map shows the forest felling at the regional level in the Nordic Region (average 2013-2015). The chart shows the forest felling by category in 1,000 m3 at the national level in the Nordic Region in 2015. On the map, the green bars indicate the average 2013-2015 forest felling. The higher the bar, the greater the forest felling in the region. The grey colour indicates regions with no data. The chart shows different forest felling categories in 1,000 m3 in 2015. The dark brown represents logs or timber, the light brown represents pulpwood, and the dark grey the energywood. The Nordic Region has a large potential for forest multi-use. Sweden and Finland have the largest forest felling in 1,000 m3, with the greatest use in logs and timber. Wood bi-products is extensively used for energy purposes and the forests display a large potential for increasing the production of renewable energy as well as other bio-based products.
2018 February
- Environment
- Nordic Region
- Others

Biogas production
These maps show the energy produced by biogas (in GWh) as well as the number of facilities producing bioenergy in the Swedish regions. The maps also show the location and type of biogas plants in Denmark, Finland, and Iceland. The brown shading indicates the produced energy in GWh in each region. The darker the brown, the larger the energy produced. The black circles are proportional to the number of facilities producing bioenergy in the Swedish region. The location of biogas plants in Denmark, Finland, and Iceland is indicated by coloured circles. The colours indicate the type of biogas plant. Biogas production is widely distributed across the Nordic Region and between the types of sources used. In 2015, 18% of the energy use in Denmark came from biomass and waste. In the western part of Denmark, biogas is mainly based on manure from farms supplemented with sludge and organic waste from wastewater plants. The vast infrastructure for gas makes it easy and accessible for farmers to link biogas to the existing energy net. The largest numbers of plants in Finland are based on farms and landfills. In 2015 in Sweden, 282 facilities produced 1947 GWh biogas with the largest regional production being in Skåne (417.5 GWh), Västra Götaland (350.9), and Stockholm (255.8). Iceland had a biogas facility in Reykjavík at Álfsnes landfill with plans for expansion in 2018.
2018 February
- Environment
- Nordic Region

Land cover 2012
This map shows the land cover in the Nordic Region in 2012. Land cover data indicates the physical land type, helping to understand the current landscape of an area. The different colours represent land cover types with urban/artificial surfaces in red, agricultural areas in orange, forests in green, scrub and herbaceous vegetation in yellow, bare ground in grey, water bodies in blue and glaciers and perpetual snow in white. There are significant differences between the Nordic countries in terms of their land use. Denmark is largely agricultural (62%), while Finland (73%), a large part of Sweden (69%) and south-eastern Norway (28%) are all dominated by forest, mainly coniferous. Iceland and the Faroe Islands have large areas of scrub and herbaceous vegetation, suitable for grazing livestock. Open land with little vegetation is significant for many regions in Norway and Iceland. Vast parts of Greenland and parts of Iceland are glaciers. The Nordic countries all have long coastlines and easy access to marine resources. The map is a Corine 2012 raster DB (V. 18.5) at 100m resolution from the European Environmental Agency and the Copernicus program, with funding by the European Union. For Faeroe Islands and Greenland the data is from GlobCover 2009 land cover, ESA 2010 and UCLouvain (harmonization by Nordregio).
2018 February
- Environment
- Nordic Region

NEET rate for young people 18-25 years in 2016
Share of young people aged 18-25 years neither in employment nor in education and training in 2016 There are a range of reasons why a young person may become part of the “NEETs” group, including (but not limited to): complex personal or family related issues; young people’s greater vulnerability in the labour market during times of economic crisis; and the growing trend towards precarious forms of employment for young people. Successful reengagement of these young people with learning and/or the labour market is a key challenge for policy makers and is vital to reducing the risk of long-term unemployment and social exclusion later in life. The map highlights two Polish regions, Podkarpackie and Warminsko-Mazurskie, as having the highest NEET rates in the BSR. High rates can also be found in several other Polish regions as well as the Northern and Eastern Finland Region. The lowest NEET rates in the Baltic Sea Region can be found in the Norwegian Capital Region, followed by several regions in Sweden, Norway and Denmark.
2017 June
- Baltic Sea Region
- Labour force

Youth unemployment rate in 2016
The map highlights two Polish regions, Podkarpackie and Lubuskie, as having the highest youth unemployment rates in the BSR. Several other regions in Poland, along with regions in Northern Finland, Central Sweden and the southernmost Swedish region of Skåne, have also been rather severely hit by youth unemployment. The lowest youth unemployment rates can be found in several Russian regions, among them St. Petersburg, and in regions in Northern Germany and Northern Norway.
2017 June
- Baltic Sea Region
- Labour force
- Nordic Region

Tertiary education among working-age population, change 2010-2015
The Nordic countries, as well as Estonia and Lithuania, have had among the highest levels of tertiary education in Europe in recent years. This map demonstrates that many regions, particularly those in Poland, are catching up. Several Lithuanian and Latvian regions have also had high rates of positive change between 2010 and 2015. The most modest growth rates, between 0 and 1.5 percent change, were experienced in two Estonian regions, one in Denmark and one in Northern Germany. Mecklenburg-Vorpommern and Brandenburg, in North-Eastern Germany, were the only regions within the Baltic Sea Region to experience a decrease in the share of working-age persons with tertiary level education from 2010-2015.
2017 March
- Baltic Sea Region
- Labour force
- Nordic Region



