83 Maps
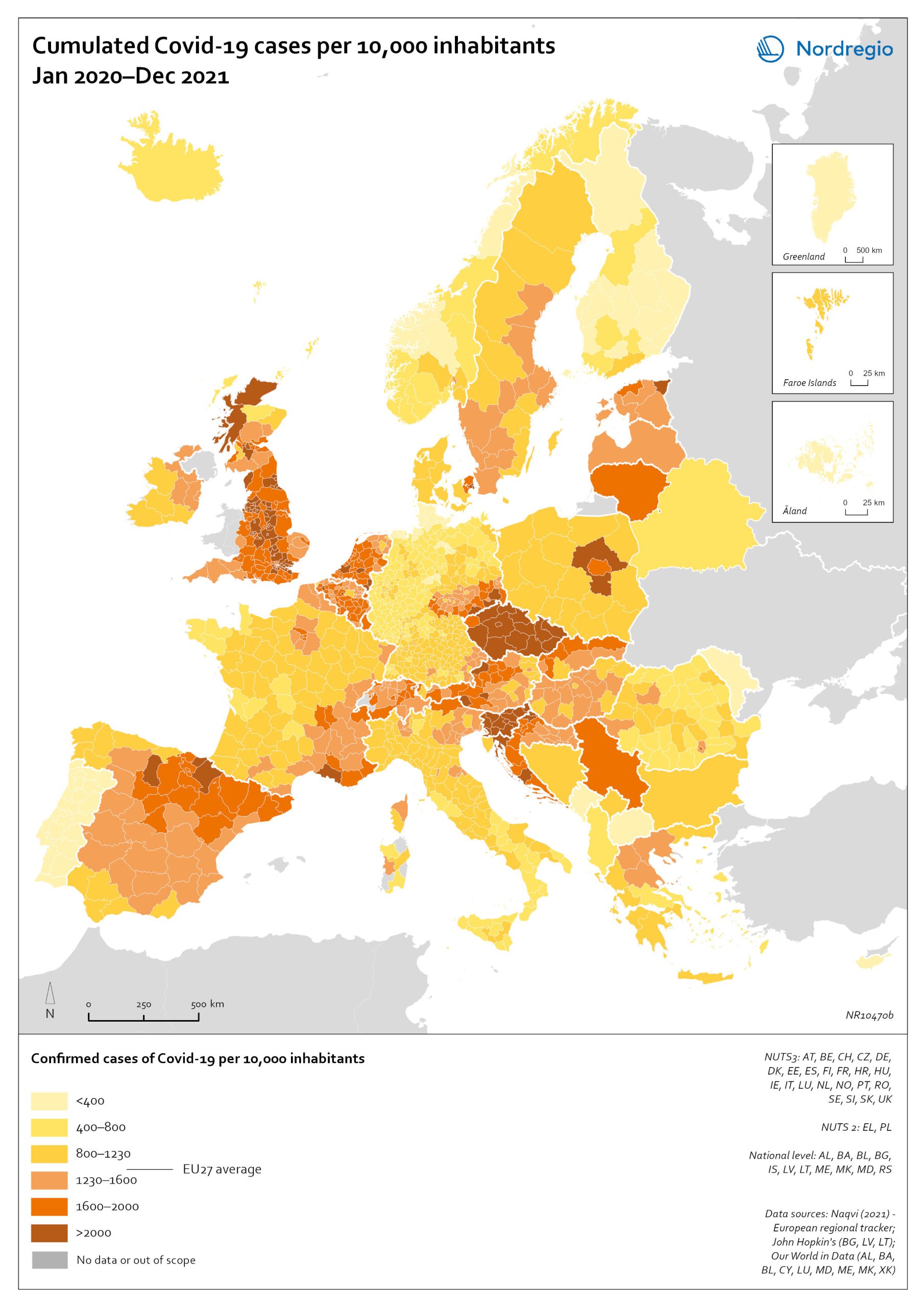
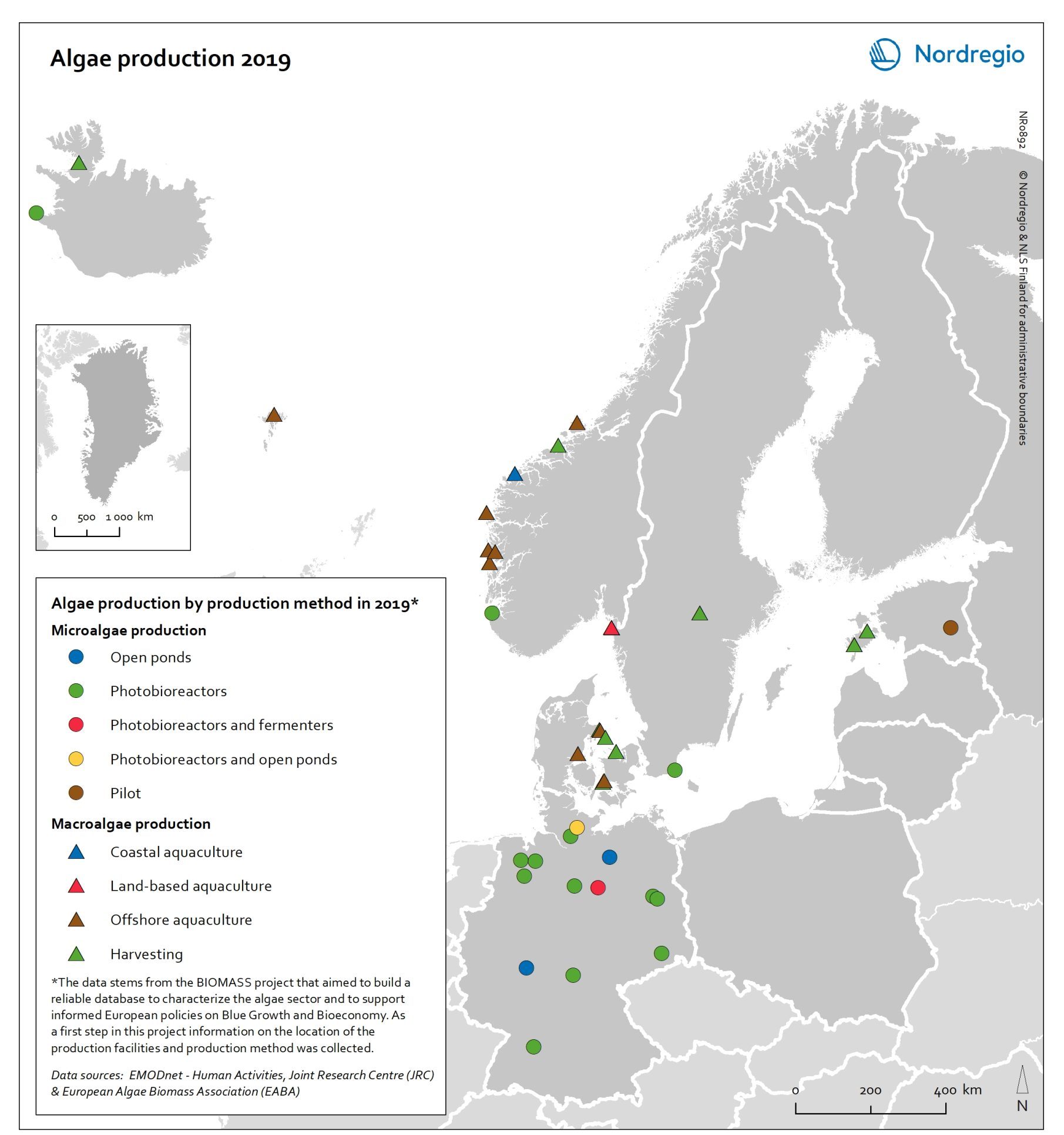
Algae production in 2019
This map shows location of algae production by production method in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region in 2019 Algae and seaweeds are gaining attention as useful inputs for industries as diverse as energy and human food production. Aquatic vegetation – both in the seas and in freshwater – can grow at several times the pace of terrestrial plants, and the high natural oil content of some algae makes them ideal for producing a variety of products, from cosmetic oils to biofuels. At the same time, algae farming has added value in potential synergies with farming on land, as algae farms utilise nutrient run-off and reduce eutrophication. In addition, aquatic vegetation is a highly versatile feedstock. Algae and seaweed thrive in challenging and varied conditions and can be transformed into products ranging from fuel, feeds, fertiliser, and chemicals, to third-generation sugar and biomass. These benefits are the basis for seaweed and algae emerging as one of the most important bioeconomy trends in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea region. The production of algae for food and industrial uses has hence significant potential, particularly in terms of environmental impact, but it is still at an early stage. The production of algae (both micro- and macroalgae) can take numerous forms, as shown by this map. At least nine different production methods were identified in the region covered in this analysis. A total of 41 production sites were operating in Denmark, Estonia, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Norway, Germany, and Sweden. Germany has by far the most sites for microalgae production, whereas Denmark and Norway have the most macroalgae sites.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Others
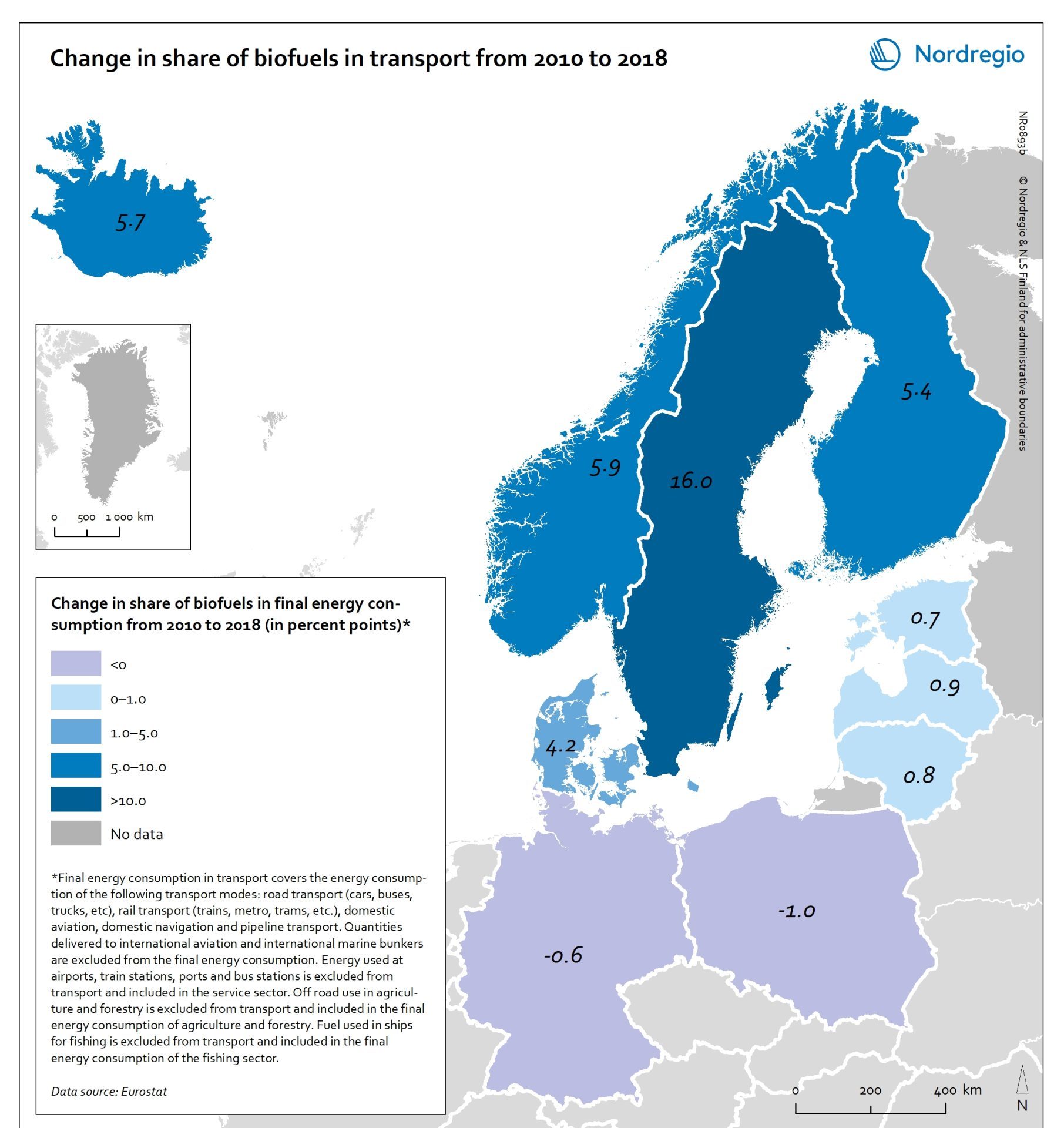
Change in share of biofuels in transport from 2010 to 2018
This map shows change in share of biofuels in final energy consumption in transport in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region from 2010 to 2018. Even though a target for greater use of biofuels has been EU policy since the Renewable Energy and Fuel Quality Directives of 2009, development has been slow. The darker shades of blue on the map represent higher increase, and the lighter shades of blue reflect lower increase. The lilac color represent decrease. The Baltic Sea represents a divide in the region, with countries to the north and west experiencing growth in the use of biofuels for transport in recent years. Sweden stands out (16 per cent growth), while the other Nordic countries has experienced more modest increase. In the southern and eastern parts of the region, the use of biofuels for transport has largely stagnated. Total biofuel consumption for transport has risen more than the figure indicates due to an increase in transport use over the period.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Transport
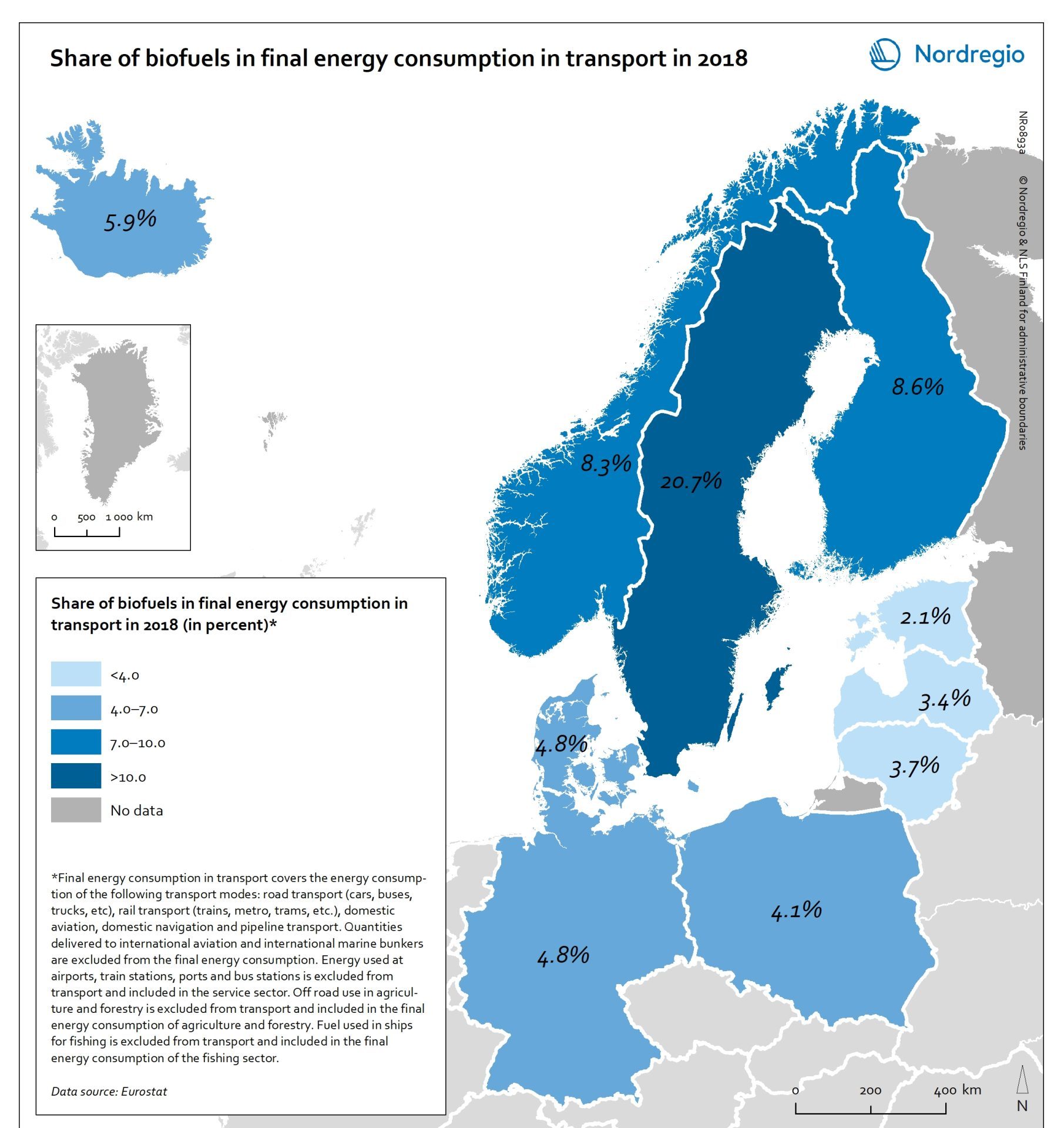
Share of biofuels in transport in 2018
This map shows the share of biofuels in final energy consumption in transport in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Sea Region in 2018. There has been considerable political support for biofuels and in the EU, this debate has been driven by the aim of reducing dependency on imported fuels. For instance, 10 per cent of transport fuel should be produced from renewable sources. The darker shades on the map represent higher proportions, and the lighter shades reflect lower proportions. As presented by the map, only Sweden (20.7%) had reached the 10 per cent target in the Nordic Arctic and Baltic Region in 2018. Both Finland (8.3%) and Norway (8.3%) were close by the target, while the other countries in the region were still lagging behind, particularly the Baltic countries.
2021 December
- Arctic
- Baltic Sea Region
- Nordic Region
- Transport

















